
 Assessing the Need
Assessing the Need
for Personal Protective Equipment:
A Guide for Small Business Employers
Small Business Safety Management Series
U.S. Department of Labor
Occupational Safety and Health Administration
OSHA 3151
1997
When must I provide eye protection for employees?
You must provide eye protection for employees whenever they are exposed to potential eye injuries during their work if work practice or engineering controls do not eliminate the risk of injury. Some of the things that might cause eye injuries include the following:
How do I select the proper protective eyewear for employees?
Begin with the following criteria:
In addition, the American National Standards Institute, Inc. (ANSI)(3) has issued standard requirements for the design, construction, testing, and use of protective devices for eyes and face.
OSHA requires that all protective eyewear you purchase for your employees meet the requirements of ANSI Z87.1-1989 for devices purchased after July 5, 1994, and ANSI Z87.1-1968 for devices purchased before that date.(4)
If employees wear eyeglasses with prescription lenses, may I consider these eye protection?
No. Eyeglasses designed for ordinary wear do not provide the level of protection necessary to protect against workplace hazards. Special care must be taken when choosing eye protectors for employees who wear eyeglasses with corrective lenses such as the following:
You also must provide protective eyewear to employees who wear contact lenses and are exposed to potential eye injury. Eye protection provided to these employees may also incorporate corrective eyeglasses. Thus, if an employee must don eyeglasses in the event of contact lens failure or loss, he or she will still be able to use the same protective eyewear.
What kind of eye and face protectors are there? What are they for?
Can face shields protect employees instead of goggles or protective spectacles?
Face shields do not protect employees from impact hazards. You may use however, face shields in combination with goggles or safety spectacles, to protect against impact hazards, even in the absence of dust or potential splashes, for additional protection beyond that offered by goggles or spectacles alone.
How do I choose the correct eye protection from among all the different types?
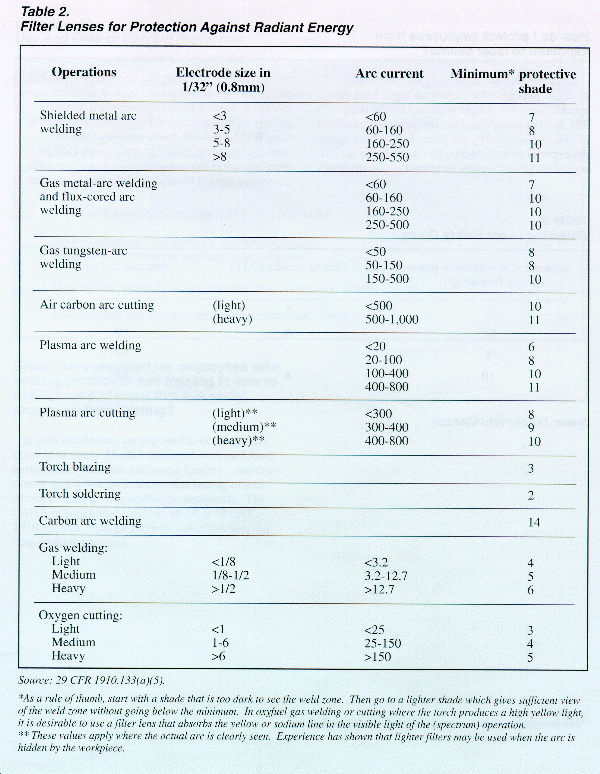
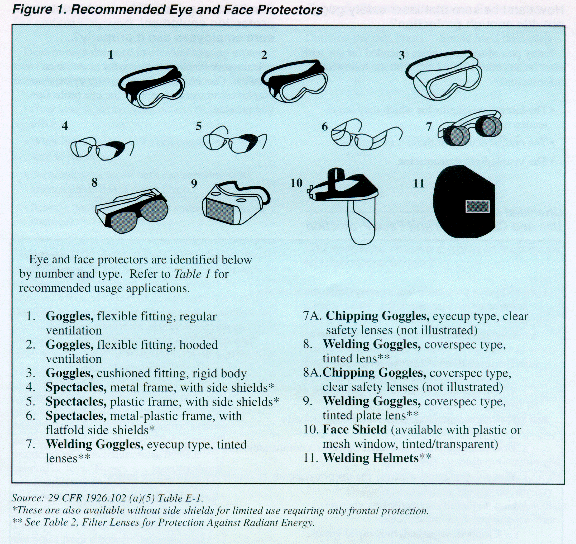
Each kind of protective eyewear is designed to protect against specific hazards. By completing the hazard assessment of your workplace outlined in the previous section, you will identify the specific workplace hazards that pose a threat to your employees' eyes and faces. Tables 1 through 3 and Figure 1 will help you find the protective devices most suited for your employees and your workplace. Locate the operations and hazards most similar to those in your workplace in Table 1 and match the number to the corresponding drawing in Figure 1. Welding and laser operations require lenses to be tinted to a degree sufficient to protect against the specific intensity of light present during that tasks your employees perform (see Tables 2 and 3).
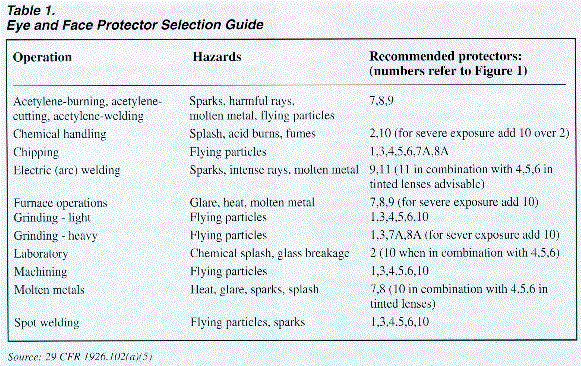
How dark do lenses on welding helmets and goggles need to be?
The intensity of light or radiant energy produced by welding, cutting, or brazing operations varies according to a number of factors including the task producing the light, the electrode size, and the arc current. Table 2 shows the minimum protective shade for a variety of welding, cutting, and brazing operations. To protect employees who are exposed to intense radiant energy, begin by selecting a shade too dark to see the welding zone. Then try lighter shades until you find one that allows a sufficient view of the welding zone without going below the minimum protective shade.
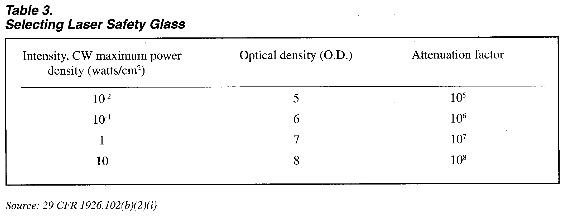
How do I protect employees from exposure to laser beams?
You must provide safety goggles specifically designed to protect the employees' eyes from the specific intensity of light produced by the laser. The level of protection will vary according the level of radiation emitted by the laser. If your employees are exposed to laser beams, you must determine the maximum power density, or intensity, that the lasers can produce.(6) Based on this knowledge, you must select lenses that will protect against this maximum intensity. Table 3 shows the minimum optical density of lenses required for various laser intensities. Employers with lasers emitting radiation between two measures of power density (or light blocking capability) must provide lenses that offer protection against the higher of the two intensities.
How can I be sure that laser safety goggles provide enough protection?
Every pair of safety goggles intended for use with laser beams must bear a label with the following information:
Once I have selected the appropriate eye protection equipment, how do I make sure employees use it properly?
Train your employees to use the protective eyewear. Checklist C will help you prepare your employees to use and care for the eye protection you provide.

My workplace gets pretty dirty. How will my employees keep their protective eyewear clean and effective?
Train your employees how to clean the eye protectors. Allow them time at the end of their shifts to do the following:
Occasionally, you must disinfect the protective eyewear. To do so, after cleaning you can do the following:
My employees work in shifts. Could I provide one pair of protective eyewear for each position instead of each employee?
Yes. If you do this, however, you must disinfect shared protective eyewear after each use. If the goggles or spectacles do not have to be individually designed to incorporate an employee's corrective lenses and you disinfect the eyewear between uses by different employees, more than one employee may use the same set of protective eyewear.
