







IPCS |
International Programme on Chemical Safety |
CHEMICAL SAFETY TRAINING MODULES
PART II: IDENTIFICATION, CLASSIFICATION AND LABELLING OF CHEMICALS
The production and use of chemicals are fundamental factors in the economic development of all countries, whether they are industrialized or developing. In one way or another, chemicals affect directly or indirectly the lives of all humans and are essential to our feeding (fertilizers, pesticides, food additives, packing), our health (pharmaceuticals, cleaning materials), or our well being (appliances, fuels, etc).
The first and most essential step leading to safe use of chemicals is to know their identity, hazards to health and the environment and the means to control them. This knowledge should be available with reasonable effort and cost. Furthermore, this inherently complex knowledge must be organized in such a way that information on the hazards and corresponding protective measures can be identified and conveyed to the user in a form that is easy to understand.
The hazard classification and labelling process is an essential tool for establishing an effective information transfer so that the degree of the hazard the chemical represents for man and the environment can be recognized, the correct preventive actions be chosen, and safe use achieved.
The International Labour Organisation (ILO) has adopted the Convention No. 170 and Recommendation No. 177 on `Safety in the use of chemicals at work' in 1990.
International, regional, and national classification and labelling systems are already established and tested in practice.
Here is described the labelling system used in the countries of European Union as an example. The United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods is also briefly presented, but more in detail in the section of Transport and Storage.
The list of chemicals with properties potential to cause major hazard is included into the section discussing the Major Hazard Chemicals.
This document consists of:
2. Identification and Classification
The objective is to identify the hazardous properties of chemicals which may constitute a risk during normal handling or use, risks to health, property or the environment. The user of the chemicals is also to be introduced to the hazards they present and given the basic information, in a suitable manner, such as using a properly made label.
In this document one component chemical is called a substance, a mixture composed of two or more substances is called a preparation.
For classification purposes the degree of hazard depends not only on the properties of a dangerous substance but also on the level of exposure. This refers to the concentration of hazardous components in the mixtures. The hazards of preparations can be assessed using the information on their component substances; for this it is essential to know also the quantities of its hazardous minor components.
The EU classification and labelling system used here as an example can be applied to dangerous substances and preparations. However, this system should not be applied to medical or veterinary products, cosmetics, munitions or explosives, pesticides specified elsewhere, waste and foodstuffs or animal feedstuffs in the finished stage. These have their own specifications and requirements for labelling.
3. What is a hazardous chemical
The following properties contribute to risk to health resulting from acute, repeated or prolonged exposure:
Fire and explosion hazards may be classified as follows
The following properties present a hazard to the environment and are:
Also substances and preparations that cannot be classified by using the above system may be regarded as dangerous if they have properties which are hazardous to health, to living organisms or if they can damage property.
4. How to pass on the information to users
All chemicals, both substances and preparations, should have a clear marking to indicate their identity.
The packages and containers of dangerous substances and preparations should, in addition to marking only, to have a label with required information.
The label should draw attention to the inherent danger to persons handling or using the chemical.
Symbols and pictograms have been established for each hazard category listed above. The symbol forms an integral part of the label and gives an immediate idea of the types of hazards that the substance or the preparation may cause. To specify the type of danger pertinent standard risk phrases should also be included in the label. Advice on the precautions necessary in the handling of chemicals are given with standard safety phrases also included in the label.
5. Where to find information about hazardous chemicals
The chemical supplier, manufacturer or importer, should be able to provide detailed information and a Safety Data Sheet.
In certain countries, such as those of the EU, the manufacturer or importer has the obligation to find and give adequate information about a chemical for assessment of the health and environmental hazards of his chemical for handling and for its labelling.
Safety data sheets have been prepared on many dangerous substances and preparations by manufacturers. These should go together with the product to the occupational user. The information in these is not always validated or checked.
On pure substances International Chemical Safety Cards are available. These contain validated basic information, which may be used also for preparing safety data sheets on chemical preparations or products.
Lists of classified chemicals exist in national legislation and regulations which provide information on local requirements in the handling of dangerous chemicals.
The information for classification, and labels, may be obtained from tests, from literature, from practical experience and from information requirements by international rules on the transport of dangerous substances and wastes.
6. How to classify for a label
The label is the basic tool to keep the user informed on the classification and the most important safety precautions. This information must be given if the preparation contains at least one substance classified as dangerous to man or the environment or if the preparation is otherwise regarded as dangerous, for example it is flammable.
In EU countries the label must clearly show
The labels should be in the national, official language(s).
The label should show the chemical names of substances that are primarily responsible for the hazards. As a general rule four chemical names on the label should be sufficient.
In some cases, more than four names may be necessary; for example all cancer causing substances in the preparation must be identified and the corresponding R- and S-phrases presented on the label.
If the preparation contains one or more of the substances requiring the following R-phrases, both the name of the substance and the R-phrase should be mentioned in the label:
R33, R39, R40, R42, R43, R45, R46, R48, R49, R60, R61, R62, R63, R64
These risks phrases are related to carcinogenic, genetic, reproductive, sensitizing and irreversible health hazards.
Four R-phrases and four S-phrases should suffice to describe the risks and to formulate the most appropriate safety advice.
Symbols showing the most serious hazards should be chosen where more than one danger symbol has to be assigned. As a general rule a maximum of two danger symbols are used.
The explanation of the letter symbols appearing in the attached lists are given below. Each letter symbol refers to a danger symbol or pictogram used in EU countries:
| Letter | Symbol | Explanation |
| E | explosive | This symbol with the word 'explosive' denotes a substance which may explode under the effect of a flame or if subjected to shocks or friction. |
| O | oxidizing | The symbol with the word 'oxidizing' refers to a substance which releases a lot of heat while it reacts with other substances, particularly flammable substances. |
| F | highly flammable | This symbol with the words 'highly flammable' denotes a substance which may become hot and finally ignite in contact with air at ambient temperature or is a solid and may readily set on fire after brief contact with the source of ignition and which continues to burn/to be consumed by chemical reaction after removal of the source of ignition. If it is gas it may burn in air at normal pressure. In contact with water or damp air the substance may release highly flammable gases in dangerous quantities. |
| F+ | extremely flammable | The same flammable symbol as above with words 'extremely flammable' denotes e.g. a liquid which would boil at body temperature and would ignite if vapours are exposed to a flame. |
| T | toxic | The symbol with skull and crossed bones with the word 'toxic' denotes a highly hazardous substance. |
| T+ | very toxic | The same symbol as above with the words 'very toxic' is used to label a substance, which, if inhaled or ingested or, if it penetrates the skin, may involve extremely serious immediate or long-term health risks and even death. |
| C | corrosive | The symbol with the word 'corrosive' will be found on a label of a substance which may destroy living tissues on contact with them. Severe burns may result from splashes of such substance. |
| Xn | harmful (less than T) | The symbol with word 'harmful' denotes to substances which may cause health hazards less than toxic. It could refer to other types of risks e.g. to allergic reactions. |
| Xi | irritant (less than C) | The same symbol as above with the word 'irritant'. |
| N | dangerous for the environment |
When more than one danger symbol is used
- the obligation to apply symbol T or T+ will make symbols C, Xn and Xi optional
- the obligation to apply symbol C will make symbols Xn and Xi optional
- the obligation to apply symbol E will make symbols F and O optional
If a preparation is classified both harmful Xn and irritant Xi, it will be labelled harmful Xn, and the irritant properties should be pointed out with appropriate R-phrases.
The total amount of the substance in the preparation has an effect in choosing the danger symbols, R- and S-phrases. (Annex 8)
Generally, no account needs to be taken of substances if they are present in following amounts, unless another lower limit has been specifically given:
Information such as "non-toxic", "not harmful" should not be used in the labels.
The pictorial symbol indicating danger is drawn in black and the background colour should be orange.
The dimensions of the label:
Capacity of the package |
Minimum dimensions in millimeters |
| Not exceeding three litres | 52x74 |
| more than three litres but not exceeding 50 litres | 74x105 |
| more than 50 litres but not exceeding 500 litres | 105x148 |
| more than 500 litres | 148x210 |
Each danger symbol must cover at least 1/10 of the surface area of the label. The minimum size of the danger symbol shall not be less than 10mm x 10mm.
Example 1. Classification of a substance
1,1,1-Trichloroethane (synonym name: methyl chloroform), used as solvent is classified as harmful Xn and dangerous to the environment N, with following R-phrases and S-phrases
| R 20 | Harmful by inhalation. |
| R 59 | Dangerous for the ozone layer. |
| S 2 | Keep out of the reach of children. |
| S 24/25 | Avoid contact with skin and eyes. |
| S 59 | Refer to manufacturer/supplier for information on recovery/recycling. |
| S 61 | Avoid release to the environment. Refer to special instructions/Safety Data Sheets. |
The label should carry this information. Check that the impurities do not exceed the limit of being noticed too as substances classified toxic.
Example 2. Classification of a preparation:
A preparation used for degreasing metal parts contains following dangerous components:
| Dangerous substance | % |
Symbol |
Risk phrases | Safety phrases |
| Trichloroethylene Xylene (flash point over 21oC) Ethanol |
23 67 8 |
Xn Xn F |
40-52/53 10-20/21-38 11 |
(2-)23-36/37-61 (2-)25 (2-)7-16 |
| Preparation | Xn |
10-20/21-38-40-52/53 | (2-)23-25-36/37-61 |
Ethanol is present below the classification level.
The R and S-phrases corresponding to the number codes are:
| R 10 | Flammable. |
| R 20/21 | Harmful by inhalation and in contact with skin. |
| R 38 | Irritating to skin. |
| R 40 | Possible risks of irreversible effects. |
| R 52/53 | Harmful to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. |
| S 23 | Do not breathe vapour. |
| S 25 | Avoid contact with eyes. |
| S 36/37 | Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves. |
| S 61 | Avoid the release to the environment. Refer to special instructions/Safety Data Sheet. |
The name, symbol, the risk phrases of the classified substance and the phrases for safety precaution are in Annex 4.
The key to have the symbol picture is in Annex 1.
The key to have a sentence in words is for the risk phrases in Annex 2. and for the safety phrases in Annex 3.
Toluene is classified in International Chemical Safety Cards: See the Cards by CAS Number, in alphabetical order or by risk phrases.
| Substance | CAS number | Symbol | Risk phrase | Safety phrase |
| TOLUENE | 108-88-3 | F, Xn | 11-20 | (2-)16-25-29-33 |
TOLUENE |
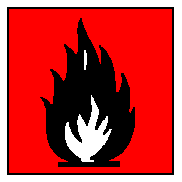 |
 |
Highly flammable |
| F Highly flammable | Xn Harmful |
| Keep out of the reach of children. Keep away from sources of ignition - No smoking. Avoid contact with eyes. Do not empty into drains. Take precautionary measures against static discharges. |
| Name and address of the manufacturer, distributor or importer. |
HAZARD CATEGORIES OF SELECTED CLASSIFICATION SYSTEMS
| HAZARD CATEGORIES | ILO |
UN RTDG |
EU |
USA |
CANADA |
| PHYSICAL HAZARDS | |||||
| compressed gas flammable explosive oxidizing reactive corrosive (materials) |
- + + + + + |
+ + + + + + |
n + + + + n |
n + + + + n |
+ + + + + + |
| HEALTH HAZARDS | |||||
| toxic (acute)* toxic (other) irritant corrosive (tissues) sensitizer carcinogen reproductive effects** mutagen |
+ + + + + + + + |
+ - - + - - - - |
+ + + + + + + + |
+ + + + + + + + |
+ + + + + + + + |
| SPECIAL HAZARDS | |||||
| environment radioactive infectious miscellaneous*** |
- - - - |
+ + + + |
+ n n n |
n n n n |
n n n n |
LEGEND:
+ : defined category
n : defined under other legislation or code
- : not defined
* : includes oral, dermal and inhalation toxicity
** : includes reproductive and developmental toxicity
*** : specific to UN RTDG; included in national transport legislation
DEFINITIONS OF DATA COMPONENTS IN LABELS IN DIFFERENT CLASSIFICATION SYSTEMS
| COMPONENTS | ILO |
UN RTDG |
EU |
USA |
CANADA |
| FORMAT | none defined | size of labels varies with transport mode. | Minimum label dimensions are defined for
different package capacities; contrasted danger symbols and background (black on yellow background); language must be that of the country where the product is put on market. |
none defined | 1. Supplier label: must appear on all controlled products received at work-places; required information must be set aside from sales information; surrounded by WHMIS border; must be printed in contrasting colours; must have all texts in English and French. 2. Workplace label: must appear on all products produced in a workplace or transferred to other containers by the employer; may appear in placard form on products received in bulk. |
| DATA ELEMENTS | 1. Trade name 2. Chemical identity 3. Supplier identi- fication. 4. Hazard symbols 5. Risk phrases 6. Safety phrases 7. Batch identifica- tion. 8. Reference to ex- isting CSDS. 9. Hazard classifi- cation. |
not mandated. The UN RTDG label defines hazards by the use of symbols, colours and danger warning words for specific hazards (explosive, radioactive, corrosive, etc.). |
1. Chemical identity 2. Hazard symbol and indication of danger. 3. Risk phrases 4. Safety phrases 5. Supplier identification (full address and tel. No.). 6. EEC number if allocated 7. the wording "EEC label" where appropriate. |
1. Chemical identity 2. Supplier identi- fication 3. Appropriate hazard warnings. Employer must ensure that labels and other forms of warning are in English and may add other languages if appropriate. |
1. Supplier label: -product identifier -supplier identification. -reference to existing CSDS. -hazard symbols; and for containers over 100 ml: -risk and safety phrases. -first aid measures 2. Workplace label: -product identifier -information for the safe handling of the products -reference to an existing CSDS. -may contain WHMIS hazard symbols or other pictograms. |
| OTHER REQUIREMENTS | Legibility, durability and size, uniformity of
labels and symbols, including colours. In general, all containers of hazardous chemicals should at least indicate the hazards of the contents through appropriate wording or symbols. |
Placarding of transport units is defined, including form, minimum size and colour of placards. | ANSI Standard Z-129.1.1988 defines acceptable precautionary phrases and hazard symbols. | Chemical name may be replaced by generic name or number in the case of products covered by provisions on exemption for confidential business information. |
Symbols and Indications of Danger Used in the Countries of EU
| E | O | |||
 |
Explosive | Oxidizing |  |
|
| F | F+ | |||
 |
Highly flammable | Extremely flammable |  |
|
| T | T+ | |||
 |
Toxic | Very toxic |  |
|
| Xn | Xi | |||
 |
Harmful | Irritant |  |
|
| C | N | |||
 |
Corrosive | Dangerous for environment |  |
Risk Phrases Used in the Countries of EU
(Phrases in parenthesis) have been deleted and are no longer in use.
Nature of Special Risks Attributed to Dangerous Substances and Preparations
| R1 | Explosive when dry. |
| R2 | Risk of explosion by shock, friction, fire or other sources of ignition. |
| R3 | Extreme risk of explosion by shock, friction, fire or other sources of ignition. |
| R4 | Forms very sensitive explosive metallic compounds. |
| R5 | Heating may cause an explosion. |
| R6 | Explosive with or without contact with air. |
| R7 | May cause fire. |
| R8 | Contact with combustible material may cause fire. |
| R9 | Explosive when mixed with combustible material. |
| R10 | Flammable. |
| R11 | Highly flammable. |
| R12 | Extremely flammable. |
| (R13 | Extremely flammable liquified gas.) |
| R14 | Reacts violently with water. |
| R15 | Contact with water liberates highly flammable gases. |
| R16 | Explosive when mixed with oxidizing substances. |
| R17 | Spontaneously flammable in air. |
| R18 | In use, may form flammable/explosive vapour-air mixture. |
| R19 | May form explosive peroxides. |
| R20 | Harmful by inhalation. |
| R21 | Harmful in contact with skin. |
| R22 | Harmful if swallowed. |
| R23 | Toxic by inhalation. |
| R24 | Toxic in contact with skin. |
| R25 | Toxic if swallowed. |
| R26 | Very toxic by inhalation. |
| R27 | Very toxic in contact with skin. |
| R28 | Very toxic if swallowed. |
| R29 | Contact with water liberates toxic gases. |
| R30 | Can become highly flammable in use. |
| R31 | Contact with acids liberates toxic gas. |
| R32 | Contact with acids liberates very toxic gas. |
| R33 | Danger of cumulative effects. |
| R34 | Causes burns. |
| R35 | Causes severe burns. |
| R36 | Irritating to eyes. |
| R37 | Irritating to respiratory system. |
| R38 | Irritating to skin. |
| R39 | Danger of very serious irreversible effects. |
| R40 | Possible risks of irreversible effects. |
| R41 | Risk of serious damage to eyes. |
| R42 | May cause sensitization by inhalation. |
| R43 | May cause sensitization by skin contact. |
| R44 | Risk of explosion if heated under confinement. |
| R45 | May cause cancer. |
| R46 | May cause heritable genetic damage. |
| (R47 | May cause birth defects.) |
| R48 | Danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure. |
| R49 | May cause cancer by inhalation. |
| R50 | Very toxic to aquatic organisms. |
| R51 | Toxic to aquatic organisms. |
| R52 | Harmful to aquatic organisms. |
| R53 | May cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. |
| R54 | Toxic to flora. |
| R55 | Toxic to fauna. |
| R56 | Toxic to soil organisms. |
| R57 | Toxic to bees. |
| R58 | May cause long-term adverse effects in the environment. |
| R59 | Dangerous for the ozone layer. |
| R60 | May impair fertility. |
| R61 | May cause harm to the unborn child. |
| R62 | Possible risk of impaired fertility. |
| R63 | Possible risk of harm to the unborn child. |
| R64 | May cause harm to breastfed babies. |
| R65 | Harmful: may cause lung damage if swallowed |
Combination of R-Phrases
| R14/15 | Reacts violently with water liberating highly flammable gases. |
| R15/29 | Contact with water liberates toxic, highly flammable gas. |
| R20/21 | Harmful by inhalation and in contact with skin. |
| R20/22 | Harmful by inhalation and if swallowed. |
| R20/21/22 | Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
| R21/22 | Harmful in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
| R23/24 | Toxic by inhalation and in contact with skin. |
| R23/25 | Toxic by inhalation and if swallowed. |
| R23/24/25 | Toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
| R24/25 | Toxic in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
| R26/27 | Very toxic by inhalation and in contact with skin. |
| R26/28 | Very toxic by inhalation and if swallowed. |
| R26/27/28 | Very toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
| R27/28 | Very toxic in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
| R36/37 | Irritating to eyes and respiratory system. |
| R36/38 | Irritating to eyes and skin. |
| R36/37/38 | Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin. |
| R37/38 | Irritating to respiratory system and skin. |
| R39/23 | Toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through inhalation. |
| R39/24 | Toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects in contact with skin. |
| R39/25 | Toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects if swallowed. |
| R39/23/24 | Toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through inhalation and in contact with skin. |
| R39/23/25 | Toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through inhalation and if swallowed. |
| R39/24/25 | Toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
| R39/23/24/25 | Toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
| R39/26 | Very toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through inhalation. |
| R39/27 | Very toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects in contact with skin. |
| R39/28 | Very toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects if swallowed. |
| R39/26/27 | Very toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through inhalation and in contact with skin. |
| R39/26/28 | Very toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through inhalation and if swallowed. |
| R39/27/28 | Very toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
| R39/26/27/28 | Very toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
| R40/20 | Harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects through inhalation. |
| R40/21 | Harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects in contact with skin. |
| R40/22 | Harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects if swallowed. |
| R40/20/21 | Harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects through inhalation and in contact with skin. |
| R40/20/22 | Harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects through inhalation and if swallowed. |
| R40/21/22 | Harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
| R40/20/21/22 | Harmful: possible risk of irreversible effects through inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
| R42/43 | May cause sensitization by inhalation and skin contact. |
| R48/20 | Harmful: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure through inhalation. |
| R48/21 | Harmful: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure in contact with skin. |
| R48/22 | Harmful: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure if swallowed. |
| R48/20/21 | Harmful: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure through inhalation and in contact with skin. |
| R48/20/22 | Harmful: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure through inhalation and if swallowed. |
| R48/21/22 | Harmful: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
| R48/20/21/22 | Harmful: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure through inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
| R48/23 | Toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure through inhalation. |
| R48/24 | Toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure in contact with skin. |
| R48/25 | Toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure if swallowed. |
| R48/23/24 | Toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure through inhalation and in contact with skin. |
| R48/23/25 | Toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure through inhalation and if swallowed. |
| R48/24/25 | Toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
| R48/23/24/25 | Toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure through inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
| R50/53 | Very toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. |
| R51/53 | Toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. |
| R52/53 | Harmful to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. |
Safety Phrases Concerning Dangerous Chemical Substances and Preparations used in the Countries of EU
(Phrases in parenthesis) have been deleted and are no longer in use.
| S1 | Keep locked up. |
| S2 | Keep out of the reach of children. |
| S3 | Keep in a cool place. |
| S4 | Keep away from living quarters. |
| S5 | Keep contents under ... (appropriate liquid to be specified by the manufacturer). |
| S6 | Keep under ... (inert gas to be specified by the manufacturer). |
| S7 | Keep container tightly closed. |
| S8 | Keep container dry. |
| S9 | Keep container in a well-ventilated place. |
| S12 | Do not keep container sealed. |
| S13 | Keep away from food, drink and animal feeding stuffs. |
| S14 | Keep away from ... (incompatible materials to be indicated by the manufacturer). |
| S15 | Keep away from heat. |
| S16 | Keep away from sources of ignition - No smoking. |
| S17 | Keep away from combustible material. |
| S18 | Handle and open container with care. |
| S20 | When using do not eat or drink. |
| S21 | When using do not smoke. |
| S22 | Do not breathe dust. |
| S23 | Do not breathe gas/fumes/vapour/spray (appropriate wording to be specified by the manufacturer). |
| S24 | Avoid contact with skin. |
| S25 | Avoid contact with eyes. |
| S26 | In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. |
| S27 | Take off immediately all contaminated clothing. |
| S28 | After contact with skin, wash immediately with plenty of ... (to be specified by the manufacturer). |
| S29 | Do not empty into drains. |
| S30 | Never add water to this product. |
| S33 | Take precautionary measures against static discharges. |
| (S34 | Avoid shock and friction.) |
| S35 | This material and its container must be disposed of in a safe way. |
| S36 | Wear suitable protective clothing. |
| S37 | Wear suitable gloves. |
| S38 | In case of insufficient ventilation, wear suitable respiratory equipment. |
| S39 | Wear eye/face protection. |
| S40 | To clean the floor and all objects contaminated by this material, use ... (to be specified by the manufacturer). |
| S41 | In case of fire and/or explosion, do not breathe fumes. |
| S42 | During fumigation/spraying, wear suitable respiratory equipment (appropriate wording to be specified by the manufacturer). |
| S43 | In case of fire, use ... (indicate in the space the precise type of fire-fighting equipment. If water increases the risk, add - Never use water). |
| (S44 | If you feel unwell, seek medical advice (show the label where possible).) |
| S45 | In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label where possible). |
| S46 | If swallowed, seek medical advice immediately and show this container or label. |
| S47 | Keep at temperature not exceeding ...C° (to be specified by the manufacturer). |
| S48 | Keep wetted with ... (appropriate material to be specified by the manufacturer). |
| S49 | Keep only in the original container. |
| S50 | Do not mix with ... (to be specified by the manufacturer). |
| S51 | Use only in well-ventilated areas. |
| S52 | Not recommended for interior use on large surface areas. |
| S53 | Avoid exposure - obtain special instructions before use. |
| (S54 | Obtain the consent of pollution control authorities before discharging to wastewater treatment plants.) |
| (S55 | Treat using the best available techniques before discharge into drains or the aquatic environment.) |
| S56 | Dispose of this material and its container at hazardous or special waste collection point. |
| S57 | Use appropriate container to avoid environmental contamination. |
| (S58 | To be disposed of as hazardous waste.) |
| S59 | Refer to manufacturer/supplier for information on recovery/recycling. |
| S60 | This material and its container must be disposed of as hazardous waste. |
| S61 | Avoid release to the environment. Refer to special instructions/Safety data sheets. |
| S62 | If swallowed do not induce vomiting: seek medical advice immediately and show this container or label. |
| Combination of S-Phrases | |
| S1/2 | Keep locked up and out of reach of children. |
| S3/7 | Keep container tightly closed in a cool place. |
| (S3/9 | Keep in a cool, well-ventilated place.) |
| (S3/7/9 | Keep container tightly closed in a cool, well-ventilated place.) |
| S3/9/14 | Keep in a cool, well-ventilated place away from ... (incompatible materials to be indicated by the manufacturer). |
| S3/9/49 | Keep only in the original container in a cool, well-ventilated place. |
| S3/9/14/49 | |
| S3/14 | Keep in a cool place away from ... (incompatible materials to be indicated by the manufacturer). |
| S7/8 | Keep container tightly closed and dry. |
| S7/9 | Keep container tightly closed and in a well-ventilated place. |
| S20/21 | When using do not eat, drink or smoke. |
| S24/25 | Avoid contact with skin and eyes. |
| S36/37 | Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves. |
| S36/39 | Wear suitable protective clothing and eye/face protection. |
| S37/39 | Wear suitable gloves and eye/face protection. |
| S36/37/39 | |
| S47/49 | Keep only in the original container at temperature not exceeding ...C° (to be specified by the manufacturer). |
| S7/47 | Keep container tightly closed and at a temperature not exceeding ...0C (to be specified by the manufacturer). |
| S29/56 | Do not empty into drains, dispose of this material and its container at hazardous or special waste collection point. |
List of Substances with Risk and Safety Phrases Used in the Countries of EU
MEANING OF NOTES A - G
| Note A | Where a substance is listed under a generic name (e.g. `...compounds' or `...salts') the correct chemical name should be stated on the label. For example for BeCl2: Beryllium chloride | |
| Note B | Some substances (acids, bases, etc.) are placed on the market
in aqueous solutions at various concentrations and therefore require different labelling
since hazards vary at different concentrations. The entries with Note B have a general
designation of the type `...% Nitric acid'. The actual concentration of the solution is
stated on the label: `45% Nitric acid. Percentages always refer to weight ratio, unless otherwise stated. Additional data (e.g. specific gravity, Baumé values) or descriptions (e.g. glacial, fuming) are permitted. |
|
| Note C | Some organic substances may be in a specific isomeric form or as a mixture of isomers with a general designation. In this case the label states clearly whether the substance is a specific isomer or a mixture of isomers. For example `Xylene' is specified: `o-Xylene' or `Xylene, m | |
| Note D | Some substances which polymerize readily or decompose spontaneously are normally placed on the market in a stabilized form. However, such substances are sometimes placed on the market in a non-stabilized form. This must be stated on the label with the name of the substance: Methacrylic acid (non-stabilized)'. | |
| Note E | Substances with specific effects on human health (classified
as carcinogenic, mutagenic and/or toxic to reproduction) if they are also classified as
`Very toxic (T+)', `Toxic (T)' or `Harmful (Xn)'. The word also shall precede the
risk phrases R20, R21, R22, R23, R24, R25, R26, R27, R28 when in a combination, for
example: R45-23: May cause cancer. Also toxic by inhalation R46-27/28: May cause heritable genetic damage. Also very toxic in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
|
| Note F | The substance may contain a stabilizer. If the stabilizer changes the hazardous properties of the substance as listed, a label must be compiled in accordance with rules for the resulting hazardous preparations. | |
| Note G | The substance may be marketed in an explosive form in which case it must be assessed using the appropriate test methods and the label should reflect its explosive property. | |
IARC List of Cancer Causing Chemicals
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION INTERNATIONAL AGENCY FOR RESEARCH ON CANCER
LISTS OF IARC EVALUATIONS ACCORDING TO IARC MONOGRAPHS
IARC, Lyon 1993
`Occupational sources' column edited by IPCS, Geneva, 1993
Any comments related to the IARC Monographs should be sent to Dr. H. Vainio,
Chief Unit of Carcinogen Identification and Evaluation, International Agency for Research on Cancer
Address: 150 cours Albert Thomas
69372 Lyon Cedex 08
France
| Group 1 | The agents and industrial processes which have been evaluated by IARC Monographs Programme as being carcinogenic to humans. |
| Group 2A | The agents and industrial processes which have been evaluated by IARC Monographs Programme as being probably carcinogenic to humans. |
| Group 2B | The agents and industrial processes which have been evaluated by IARC Monographs Programme as being possibly carcinogenic to humans. |
Group 1: CARCINOGENIC TO HUMANS
Substances
| Agent/Industrial process | CAS Number | Occupational sources |
| Aflatoxins (1993)a | 1402-68-2 | Feedstuff contaminants, mycotoxins |
| 4-Aminobiphenyl | 92-67-1 | Rubber manufacture |
| Arsenic and arsenic compoundsb | 7440-38-2 | Drug, pesticide |
| Asbestos | 1332-21-4 | Roofing, friction material |
| Azathioprine | 446-86-6 | Drug |
| Benzene | 71-43-2 | Solvent, raw material |
| Benzidine | 92-87-5 | Raw material, impurity |
| Beryllium and beryllium compoundsd | 7440-41-7 | Raw material, electronics industry |
| N,N-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-2-naphthylamine (Chlornaphazine) | 494-03-1 | Drug |
| Bis(chloromethyl)ether and | 542-88-1 | Laboratory chemical |
| chloromethyl methyl ether (technical-grade) | 107-30-2 | |
| 1,4-Butanediol dimethanesulfonate (Myleran) | 55-98-1 | Antineoplastic agent |
| Cadmium and cadmium compoundsd | 7440-43-9 | Raw material |
| Chlorambucil | 305-03-3 | Antineoplastic agent |
| 1-(2-Chloroethyl)-3-(4-methylcyclohexyl)-1- nitrosourea (Methyl-CCNU) | 13909-09-6 | Antineoplastic agent |
| Chromium(VI) compounds (1990) | Pigment manufacturing | |
| Ciclosporin (1990) | 79217-60-0 | Drug |
| Cyclophosphamide | 50-18-0 | Antineoplastic agent |
| Diethylstilboestrol | 56-53-1 | Drug |
| Erionite | 66733-21-9 | Natural mineral fibre |
| Melphalan | 148-82-3 | Antineoplastic agent |
| 8-Methoxypsoralen (Methoxsalen) plus ultraviolet radiation | 298-81-7 | Dermatological drug |
| MOPP and other combined chemotherapy including alkylating agents | Antineoplastic agents | |
| Mustard gas (Sulfur mustard) | 505-60-2 | War gas |
| 2-Naphthylamine | 91-59-8 | Dye manufacturing |
| Nickel compounds (1990) | Pigment, batteries, impurity | |
| Oestrogen replacement therapy | Hormones |
| Oestrogens, nonsteroidalb | Hormones, pharmaceutical industry | |
| Oestrogens, oesteroidalb | Hormones, pharmaceutical industry | |
| Oral contraceptives, combinedc | Hormones | |
| Oral contraceptives, sequential | Hormones | |
| Radon and its decay products (1988) | 10043-92-2 | Mining |
| Solar radiation (1992) | ||
| Talc containing asbest-form fibres | Extenders in paints and ceramic products | |
| Thiotepa (1990) | 52-24-4 | Antineoplastic agent |
| Treosulfan | 299-75-2 | Antineoplastic agent |
| Vinyl chloride (monomer) | 75-01-4 | Plastic industry |
Mixtures
| Agent/Industrial process | CAS Number | Occupational sources |
| Alcoholic beverages (1988) | ||
| Analgesic mixtures containing phenacetin | Drugs | |
| Betel quid with tobacco | ||
| Coal-tar pitches | 65996-93-2 | Raw material |
| Coal-tars | 8007-45-2 | Drug, raw material |
| Mineral oils, untreated and mildly treated | Use of crude oil distillates | |
| Salted fish (Chinese-style) (1993) | ||
| Shale-oils | 68308-34-9 | |
| Soots | ||
| Tobacco products, smokeless | ||
| Tobacco smoke |
Group 2 A: PROBABLY CARCINOGENIC TO HUMANS
Substances
| Agent/Industrial process | CAS Number | Occupational sources |
| Acrylonitrile | 107-13-1 | Raw material |
| Adriamycind | 23214-92-8 | Antineoplastic agent |
| Androgenic (anabolic) steroids | Drugs | |
| Azacitidine (1990)d | 320-67-2 | Antineoplastic agent |
| Benz[a]anthracened | 56-55-3 | Impurity |
| Benzidine-based dyesd | Dyes | |
| Benzo[a]pyrened | 50-32-8 | Impurity |
| Bischloroethyl nitrosourea (BCNU) | 154-93-8 | Antineoplastic agent |
| 1,3-Butadiene (1992) | 106-9-90 | Manufacture of synthetic rubber |
| Captafol (1991)d | 2425-06-1 | Fungicides, pesticides /1.,pp.927-1616/ |
| Chloramphenicol (1990)d | 56-75-7 | Antibiotics |
| 1-(2-Chloroethyl)-3-cyclohexyl- | ||
| 1-nitrosourea (CCNU)d | 13010-47-4 | Antineoplastic agent |
| para-Chloro-ortho-toluidine and | ||
| its strong acid salts (1990)d | 95-69-2 | Synthesis of organic dyestuffs |
| Chlorozotocin (1990)d | 54749-90-5 | Antineoplastic agent |
| Cisplatind | 15663-27-1 | Antineoplastic agent |
| Dibenz[a,h]anthracened | 53-70-3 | Coal-tar |
| Diethyl sulfate (1992)d | 64-67-5 | Raw material, laboratories |
| Dimethylcarbamoyl chlorided | 79-44-7 | Laboratories |
| Dimethyl sulfated | 77-78-1 | Raw material, laboratories |
| Epichlorohydrind | 106-89-8 | Epoxyresin products, raw material, laboratories |
| Ethylene dibromided | 106-93-4 | Soil fumigant, leaded gasoline |
| Ethylene oxide | 75-21-8 | Pesticide, intermediate |
| N-Ethyl-N-nitrosouread | 759-73-9 | Laboratory synthesis of diazoethane |
| Formaldehyde | 50-00-0 | Preservative, disinfectant, textile, wood/timber industry, raw material |
| IQd (2-Amino-3-methylimid- | ||
| azo[4,5-f]-quinoline) (1993) | 76180-96-6 | Grilled fish and meat |
| 5-Methoxypsoralend | 484-20-8 | Dermatological agent |
| 4,4'-Methylene bis(2-chloroaniline) | ||
| (MOCA) (1993)101-14-4 | Polyurethane industry, curing agent | |
| N-Methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (MNNG)d | 70-25-7 | Laboratory agent |
| N-Methyl-N-nitrosouread | 684-93-5 | Laboratory synthesis of diazomethane |
| Nitrogen mustard | 51-75-2 | Basis for some antineoplastic agents |
| N-Nitrosodiethylamined | 55-18-5 | Laboratories |
| N-Nitrosodimethylamined | 62-75-9 | Laboratories, pollutant |
| Phenacetin | 62-44-2 | Drug |
| Procarbazine hydrochlorided | 366-70-1 | Antineoplastic agent |
| Propylene oxided | 75-56-9 | Production of propylene glycol |
| Silica, crystalline | 14808-60-7 | Ceramic industry |
| Styrene oxide | 96-09-3 | Epoxy resin additive |
| Tris(2,3-dibromopropyl)phosphate | 126-72-7 | |
| Ultraviolet radiation A (1992)d | Solar radiation | |
| Ultraviolet radiation B (1992)d | Solar radiation | |
| Ultraviolet radiation C (1992)d | Welding operation, laser | |
| Vinyl bromided | 593-60-2 | As an intermediate in organic synthesis, manufacture of polymers |
Mixtures
| Agent/Industrial process | CAS Number | Occupational sources |
| Creosotes | 8001-58-9 | Wood preservative for roofing |
| Diesel engine exhaust (1989) | ||
| Hot mate (1991) | Beverage | |
| Non-arsenical insecticides, spraying and | ||
| Occupational exposures in application of (1991) | ||
| Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) | 1336-36-3 | Limited application in capacitors |
Group 2B: POSSIBLY CARCINOGENIC TO HUMANS
Substances
| Agent/Industrial process | CAS Number | Occupational sources |
| A-a-C; (2-Amino-9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole) | 26148-68-5 | Grilled food, tobacco smoke |
| Acetaldehyde | 75-07-0 | Manufacture of acetic acid and ethyl acetate |
| Acetamide | 60-35-5 | As a solvent for organic compounds, plasticizer |
| Acrylamide | 79-06-1 | Manufacture of acrylamide polymers |
| AF-2;[2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)-acrylamide] | 3688-53-7 | Ex-food preservative |
| Aflatoxin M1 (1993) | 6795-23-9 | Found in the milk cows fed toxic meals |
| para-Aminoazobenzene | 60-09-3 | Dyes |
| ortho-Aminoazotoluene | 97-56-3 | Dyes |
| 2-Amino-5-(5-nitro-2-furyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazole | 712-68-5 | Drug |
| Amitrole | 61-82-5 | Herbicide |
| ortho-Anisidine | 90-04-0 | Laboratories |
| Antimony trioxide (1989) | 1309-64-4 | Tartar emetic, paint pigment |
| AramiteR | 140-57-8 | Pesticide |
| Atrazine (1991) | 1912-24-9 | Herbicide |
| Auramine (technical-grade) | 492-80-8 | Dye manufacture |
| Azaserine | 115-02-6 | Antineoplastic agent |
| Benzo[b]fluoranthene | 205-99-2 | Impurity |
| Benzo[j]fluoranthene | 205-82-3 | Impurity |
| Benzo[k]fluoranthene | 207-08-9 | Impurity |
| Benzyl violet 4B | 1694-09-3 | Textile dye |
| Bleomycinse | 11056-06-7 | Antineoplastic drug |
| Bracken fern | ||
| Bromodichloromethane (1991) | 75-27-4 | Intermediate solvent |
| Butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) | 25013-16-5 | Food additive |
| ß--Butyrolactone | 3068-88-0 | Laboratories |
| Caffeic acid (1993) | 331-39-5 | Constituent of plants |
| Carbon-black extracts | Manufacture of natural and synthetic rubber | |
| Carbon tetrachloride | 56-23-5 | Solvent, raw material |
| Ceramic fibres (1988) | Use in manufacture of paper felts, furnace | |
| Chlordane (1991) | 57-74-9 | Pesticide |
| Chlordecone (Kepone) | 143-50-0 | Pesticide |
| Chlorendic acid (1990) | 115-28-6 | Chemical intermediate in the manufacture of unsaturated polyester resins |
| a-Chlorinated toluenes | Intermediates | |
| para-Chloroaniline (1993) | 106-47-8 | Dye industry |
| Chloroform | 67-66-3 | Solvent, raw material |
| Chlorophenols | Fungicides, bactericides | |
| Chlorophenoxy herbicides | Herbicides | |
| 4-Chloro-ortho-phenylenediamine | 95-83-0 | Hair-dye component |
| CI Acid Red 114 (1993) | 6459-94-5 | Dye |
| CI Basic Red 9 (1993) | 569-61-9 | Dye |
| CI Direct Blue 15 (1993) | 2429-74-5 | Dye |
| Citrus Red No. 2 (CI 12156) | 6358-53-8 | Dye |
| Cobalt and cobalt compounds (1991) | 7440-48-4 | Manufacture of magnets |
| para-Cresidine | 120-71-8 | Dye manufacturing |
| Cycasin | 14901-08-7 | Naturally occurring toxin, seeds, roots and leaves of cycad plants |
| Dacarbazine | 4342-03-4 | Antineoplastic drug |
| Dantron | ||
| (Chrysazin; 1,8-Dihydroxyanthraquinone) (1990) | 117-10-2 | Drug |
| Daunomycin | 20830-81-3 | Antineoplastic agent |
| DDT (para,para'-DDT) (1991) | 50-29-3 | Pesticide |
| N,N'-Diacetylbenzidine | 613-35-4 | Dye manufacturing |
| 2,4-Diaminoanisole | 615-05-4 | Dye manufacturing, hair dye |
| 4,4'-Diaminodiphenyl ether | 101-80-4 | Dye manufacturing |
| 2,4-Diaminotoluene | 95-80-7 | Dye manufacturing, raw material, hair dye |
| Dibenz[a,h]acridine | 226-36-8 | Pollutant |
| Dibenz[a,j]acridine | 224-42-0 | Pollutant |
| 7H-Dibenzo[c,g]carbazole | 194-59-2 | Tobacco smoke |
| Dibenzo[a,e]pyrene | 192-65-4 | Diesel and gasoline engine exhaust fumes |
| Dibenzo[a,h]pyrene | 189-64-0 | Diesel and gasoline engine exhaust fumes |
| Dibenzo[a,i]pyrene | 189-55-9 | Diesel and gasoline engine exhaust fumes |
| Dibenzo[a,l]pyrene | 191-30-0 | Diesel and gasoline engine exhaust fumes |
| 1,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane | 96-12-8 | Pesticide |
| para-Dichlorobenzene | 106-46-7 | Fumigants, insecticides |
| 3,3'-Dichlorobenzidine | 91-94-1 | Raw material, dye manufacturing |
| 3,3'-Dichloro-4,4'-diaminodiphenyl ether | 28434-86-8 | Dye, raw material |
| 1,2-Dichloroethane | 107-06-2 | Solvent, raw material |
| Dichloromethane (Methylene chloride) | 75-09-2 | Solvent |
| 1,3-Dichloropropene (technical-grade) | 542-75-6 | Pesticides |
| Dichlorvos (1991) | 62-73-7 | Pesticide |
| Diepoxybutane | 1464-53-5 | Raw material, laboratories |
| Di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate | 117-81-7 | Plastic industry |
| 1,2-Diethylhydrazine | 1615-80-1 | Laboratory chemical |
| Diglycidyl resorcinol ether | 101-90-6 | Epoxy resin, aircraft equipment industry |
| Dihydrosafrole | 94-58-6 | Chemical intermediate for manufacture of piperonyl butoxide |
| Diisopropyl sulfate (1992) | 2973-10-6 | Manufacturing of isopropanol |
| 3,3'-Dimethoxybenzidine (ortho-Dianisidine) | 119-90-4 | Dye, laboratories |
| para-Dimethylaminoazobenzene | 60-11-7 | Dye, laboratories |
| trans-2-[(Dimethylamino)methylimino]-5-[2-(5-nitro- | ||
| 2-furyl)-vinyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazole | 25962-77-0 | Limited usage as a pharmaceutical |
| 2,6-Dimethylaniline (2,6-Xylidine) (1993) | 87-62-7 | Synthesis of other chemicals |
| 3,3'-Dimethylbenzidine (ortho-Tolidine) | 119-93-7 | Dye, laboratories |
| Dimethylformamide (1989) | 68-12-2 | Solvent for liquids and organic compounds |
| 1,1-Dimethylhydrazine | 57-14-7 | Rocket fuel formulations, chemical synthesis |
| 1,2-Dimethylhydrazine | 540-73-8 | Chemical intermediate |
| 1,6-Dinitropyrene (1989) | 42397-64-8 | Diesel and gasoline engine exhaust fumes |
| 1,8-Dinitropyrene (1989) | 42397-65-9 | Diesel and gasoline engine exhaust fumes |
| 1,4-Dioxane | 123-91-1 | Raw material, solvent |
| Disperse Blue 1 (1990) | 2475-45-8 | Dye, hair dye |
| Ethyl acrylate | 140-88-5 | As a component of solution for coating textiles, paper and leather |
| Ethylene thiourea | 96-45-7 | Raw material, laboratories, rubber industry |
| Ethyl methanesulfonate | 62-50-0 | Laboratories |
| 2-(2-Formylhydrazino)-4-(5-nitro-2-furyl)thiazole | 3570-75-0 | No use |
| Glasswool (1988) | ||
| Glu-P-1 (2-Amino-6- | ||
| methyldipyrido[1,2-a:3',2'-d]imidazole) | 67730-11-4 | Charred fraction of cooked fish and meat |
| Glu-P-2 (2-Aminodipyrido[1,2-a:3',2'-d]imidazole) | 67730-10-3 | Charred fraction of cooked fish and meat |
| Glycidaldehyde | 765-34-4 | Acrolein metabolite |
| Griseofulvin | 126-07-8 | Antibiotic drug, veterinary medicine |
| HC Blue No. 1 (1993) | 2784-94-3 | Hair dye |
| Heptachlor (1991) | 76-44-8 | Pesticide |
| Hexachlorobenzene | 118-74-1 | Fungicide |
| Hexachlorocyclohexanes | Pesticide | |
| Hexamethylphosphoramide | 680-31-9 | Solvent |
| Hydrazine | 302-01-2 | Raw material |
| Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene | 193-39-5 | Tobacco smoke, inhalation of polluted air |
| Iron-dextran complex | 9004-66-4 | Drug |
| Lasiocarpine | 303-34-4 | Used medicinally as an emetic and in the treatment of snake bites |
| Lead [7439-92-1] and lead compounds, inorganic | Manufacture of pipes, cable sheating /1.,p.1200/ | |
| Magenta (containing CI Basic Red 9) (1993) | 632-99-5 | Dyes and dyestuff |
| MeA-a-C (2-Amino-3-methyl- | ||
| 9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole) | 68006-83-7 | Grilled food, tobacco smoke |
| Medroxyprogesterone acetate | 71-58-9 | Hormones, pharmaceutical industry |
| MeIQ (1993) | ||
| (2-Amino-3,4-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline) | 77094-11-2 | Grilled beef and fish |
| MeIQx (1993) | ||
| (2-Amino 3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline) | 77500-04-0 | Fried fish and beef |
| Merphalan | 531-76-0 | Antineoplastic agent |
| 2-Methylaziridine | 75-55-8 | Intermediate |
| Methylazoxymethanol acetate | 592-62-1 | Cancer research |
| 5-Methylchrysene | 3697-24-3 | Diesel and gasoline engine exhaust fumes |
| 4,4'-Methylene bis(2-methylaniline) | 838-88-0 | Dye manufacture |
| 4,4'-Methylenedianiline | ||
| (4,4'-Diaminodiphenylmethane) | 101-77-9 | Production of isocyanates and polyisocyanates |
| Methylmercury compounds (1993) | ||
| Methyl methanesulfonate | 66-27-3 | Produced for research purposes |
| 2-Methyl-1-nitroanthraquinone (uncertain purity) | 129-15-7 | Dye intermediate |
| N-Methyl-N-nitrosourethane | 615-53-2 | Laboratory chemical |
| Methylthiouracil | 56-04-2 | Antineoplastic agent |
| Metronidazole | 443-48-1 | Drug |
| Mirex | 2385-85-5 | Pesticides |
| Mitomycin C | 50-07-7 | Antineoplastic agent |
| Monocrotaline | 315-22-0 | Consumptions of extracts of crotalaria species as bush teas |
| 5-(Morpholinomethyl)- | ||
| 3-[(5-nitrofurfurylidene)amino]-2-oxazolidinone | 3795-88-8 | Former drug |
| Nafenopin | 3771-19-5 | Drug |
| Nickel, metallic (1990) | 7440-02-0 | Manufacture of acid-resisting and magnetic alloys |
| Nitridazole | 61-57-4 | Drug |
| Nitrilotriacetic acid and its salts (1990) | 139-13-9 | Softener in cleaning agents and phosphate substitute in detergents |
| 5-Nitroacenaphthene | 602-87-9 | Diesel exhaust |
| 6-Nitrochrysene (1989) | 7496-02-8 | Gasoline and diesel engine exhaust fumes |
| Nitrofen, technical-grade | 1836-75-5 | Herbicide |
| 2-Nitrofluorene (1989) | 607-57-8 | Gasoline and diesel engine exhaust fumes |
| 1-[(5-Nitrofurfurylidene)amino]-2-imidazolidinone | 555-84-0 | Former drug |
| N-[4-(5-Nitro-2-furyl)-2-thiazolyl]acetamide | 531-82-8 | Analgesics, anti-inflammatory agent |
| Nitrogen mustard N-oxide | 126-85-2 | Intermediate in production of antineoplastic drugs |
| 2-Nitropropane | 79-46-9 | Use in vinyl epoxy paints, printing inks, adhesives |
| 1-Nitropyrene (1989) | 5522-43-0 | Diesel engine exhaust fumes |
| 4-Nitropyrene (1989) | 57835-92-4 | Laboratory chemical |
| N-Nitrosodi-n-butylamine | 924-16-3 | |
| N-Nitrosodiethanolamine | 1116-54-7 | Isolated from cosmetic products |
| N-Nitrosodi-n-propylamine | 621-64-7 | Isolated in some pesticides |
| 3-(N-Nitrosomethylamino)propionitrile | 60153-49-3 | Constitutent of betel nut |
| 4-(N-Nitrosomethylamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone | ||
| (NNK) | 64091-91-4 | Tobacco smoke |
| N-Nitrosomethylethylamine | 10595-95-6 | Tobacco smoke |
| N-Nitrosomethylvinylamine | 4549-40-0 | Apple brandy |
| N-Nitrosomorpholine | 59-89-2 | Rubber industry |
| N'-Nitrosonornicotine | 16543-55-8 | Tobacco smoke |
| N-Nitrosopiperidine | 100-75-4 | Fried meat and fish, rubber |
| N-Nitrosopyrrolidine | 930-55-2 | Tobacco smoke, fried meat and fish |
| N-Nitrososarcosine | 13256-22-9 | Fried meat |
| Ochratoxin A (1993) | 303-47-9 | Mycotoxin |
| Oil Orange SS | 2646-17-5 | Dye |
| Panfuran S, containing dihydroxymethylfuratrizine | 794-93-4 | Drug |
| Pentachlorophenol (1991) | 87-86-5 | Pesticide |
| Phenazopyridine hydrochloride | 136-40-3 | Drug |
| Phenobarbital | 50-06-6 | Drug |
| Phenoxybenzamine hydrochloride | 63-92-3 | Drug |
| Phenyl glycidyl ether (1989) | 122-60-1 | Epoxy compounds |
| Phenytoin | 57-41-0 | Drug |
| PhIP (2-Amino-1-methyl- | ||
| 6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine) (1993) | 105650-23-5 | Cooked food, tobacco smoke |
| Ponceau MX | 3761-53-3 | Dye |
| Ponceau 3R | 3564-09-8 | Dye |
| Potassium bromate | 7758-01-2 | Flour milling industries as additive to improve baking properties |
| Progestins | Drugs | |
| 1,3-Propane sultone | 1120-71-4 | Sulfopropylation of organic compounds |
| ß-Propiolactone | 57-57-8 | Used in organic synthesis, vapour sterilizer, disinfectant |
| Propylthiouracil | 51-52-5 | Antineoplastic agent |
| Rockwool (1988) | ||
| Saccharin | 81-07-2 | Artificial sweeteners |
| Safrole | 94-59-7 | Parfumery, soaps, flavouring agent in drugs |
| Slagwool (1988) | ||
| Sodium ortho-phenylphenate | 132-27-4 | Fungicide |
| Sterigmatocystin | 10048-13-2 | Mycotoxin |
| Streptozotocin | 18883-66-4 | Drug |
| Styrenee | 100-42-5 | Solvent, raw material |
| Sulfallate | 95-06-7 | Herbicide |
| 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-para-dioxin (TCDD) | 1746-01-6 | By-product during the synthesis of 2,4,5-trichlorophenol |
| Tetrachloroethylene | 127-18-4 | Dry cleaning |
| Thioacetamide | 62-55-5 | Use as an analytical reagent in the laboratory |
| 4,4'-Thiodianiline | 139-65-1 | Dye intermediate |
| Thiourea | 62-56-6 | Photocopying, raw material |
| Toluene diisocyanates | 26471-62-5 | Manufacture of elastomers of polyuretane |
| ortho-Toluidine | 95-53-4 | Dye |
| Trichlormethine (Trimustine hydrochloride) (1990) | 817-09-4 | Antineoplastic agent |
| Trp-P-1 | ||
| (3-Amino-1,4-dimethyl-5H-pyrido[4,3-b]indole) | 62450-06-0 | Charred fraction of cooked fish and meat |
| Trp-P-2 | ||
| (3-Amino-1-methyl-5H-pyrido[4,3-b]indole) | 62450-07-1 | Charred fraction of cooked fish and meat |
| Trypan blue | 72-57-1 | Dye |
| Uracil mustard | 66-75-1 | Antineoplastic agent |
| Urethane | 51-79-6 | Raw material |
Mixtures
| Agent/Industrial process | CAS Number | Occupational sources |
| Bitumens, extracts of steam-refined and air-refined | 8052-42-4 | |
| Carrageenan, degraded | 9000-07-1 | Food additive |
| Chlorinated paraffins of average carbon chain length C12 | ||
| and average degree of chlorination approximately 60% (1990) | ||
| Coffee (urinary bladder) (1991) | ||
| Diesel fuel, marinee (1989) | ||
| Engine exhaust, gasoline (1989) | ||
| Fuel oils, residual (heavy) (1989) | ||
| Gasolinee (1989) | ||
| Pickled vegetables (traditional in Asia) (1993) | ||
| Polybrominated biphenyls (Firemaster BP-6) | 59536-65-1 | Flame retardant |
| Toxaphene (Polychlorinated camphenes) | 8001-35-2 | Pesticide |
| Toxins derived from Fusarium moniliforme (1993) | Mycotoxins | |
| Welding fumes (1990) |
List of chemicals banned or severely restricted to certain uses owing to their effects on health and the environment in the countries of EU
| Chemical | CAS Number | Use category | Use limitation |
| MERCURIC OXIDE | 21908-53-2 | P | SR |
| MERCUROUS CHLORIDE | 10112-91-1 | P | SR |
| OTHER INORGANIC MERCURY COMPOUNDS | P | B | |
| ALKYL MERCURY COMPOUNDS | P | SR | |
| ALKOXYALKYL AND ARYL MERCURY COMPOUNDS | P | B | |
| ALDRIN | 309-00-2 | P | SR |
| CHLORDANE | 57-74-9 | P | B |
| DIELDRIN | 60-57-1 | P | B |
| DDT | 50-29-3 | P | B |
| ENDRIN | 72-20-8 | P | SR |
| HCH (contains < 99% gamma isomer) | 608-73-1 | P | B |
| HEPTACHLOR | 74-44-8 | P | B |
| HEXACHLOROBENZENE | 118-74-1 | P | B |
| CAMPHECHLOR (TOXAPHENE) | 8001-35-2 | P | B |
| POLYCHLORINATED BIPHENYLS (PCB), except MONO- and DICHLORINATED BIPHENYLS | 1336-36-3 | I | B |
| POLYCHLORINATED TERPHENYLS (PCT) | 61788-33-8 | I | B |
| PREPARATIONS with a PCB or PCT content higher than 0.01% by weight | I | B | |
| TRIS(2,3-DIBROMOPROPYL) PHOSPHATE | 126-72-7 | I | SR |
| TRIS-AZIRIDINYL-PHOSPHIOXIDE | 545-55-1 | I | SR |
| POLYBROMINATED BIPHENYLS (PBB) CROCIDOLITE | 12001-28-4 | I | SR |
| NITROFEN | 1836-75-5 | P | B |
| 1,2-DIBROMOETHANE | 106-93-4 | P | B |
| 1,2-DICHLOROETHANE | 107-06-2 | P | B |
| AMOSITE | 12172-73-5 | B | |
| ANTHOPHYLLITE ASBESTOS | 77536-67-5 | B | |
| ACTINOLITE ASBESTOS | 77536-66-4 | B | |
| TREMOLITE ASBESTOS | 77536-68-6 | B | |
| CADMIUM and its compounds | 7440-43-9 | R | |
| 2-NAPHTYLAMINE and its salts | 91-59-8 | B | |
| 4-AMINOPHENYL and its salts | 92-67-1 | B | |
| BENZIDINE and its salts | 92-87-5 | B | |
| 4-NITROPHENYL | 92-93-3 | B |
LEGEND:
Use category:
P: plant-protection product
I: industrial chemical
Use limitation:
SR: severe restriction
B: ban
R: restrictions