 |
  |
By William J. Zeile
|
US Bureau of Economic
Analysis |
Introcution
Trends in Intrafirm Trade
Industry Patterns of Intrafirm
Trade
Intrafirm trade with MOFA's
Intrafirm trade of U.S.
affiliates
Geographic Patterns of
Intrafirm Trade
Intrafirm trade shares
Relation to
trading-partner income levels
Cross-border transactions between affiliated units of multinational companies account for a major share of U.S. international trade in goods. In 1994, these transactions—commonly referred to as "intrafirm trade"—accounted for more than one-third of U.S. exports of goods and for more than two-fifths of U.S. imports of goods.
As an aspect of the growing integration of the world economy, intrafirm trade has attracted considerable interest in recent years, particularly in the wake of the surge in international direct investment in the late 1980's./1/ Intrafirm trade plays a critical role in the operations of multinational companies (MNC's): It may help an MNC to reduce the costs of distributing goods abroad or of acquiring inputs from abroad or to integrate production processes on a global scale. Intrafirm trade may respond differently than trade between unrelated parties to changes in economic conditions; for example, it may—at least in the short term—be more insulated from competitive forces in particular markets or from overall changes in prices, exchange rates, or general economic conditions. Furthermore, the prices—often termed "transfer prices"—that govern intrafirm trade may have their own unique characteristics and determinants.
In a previous SURVEY OF CURRENT BUSINESS article, BEA presented aggregate estimates of U.S. intrafirm exports and imports of goods and services for 1982–93./2/ A disaggregation of the intrafirm-export and -import totals into the trade between U.S. parent companies and their foreign affiliates and the trade between foreign-owned U.S. affiliates and their foreign parent groups showed that intrafirm exports largely consisted of transactions by U.S. MNC's, whereas intrafirm imports largely consisted of transactions by foreign MNC's.
This article presents a more detailed examination of U.S. intrafirm trade in goods by U.S. MNC's and by foreign MNC's operating in the United States./3/ The intrafirm transactions are disaggregated by industry of affiliate, by country of destination or origin, and for foreign MNC's, by country of ownership.
In much of the discussion, the U.S. intrafirm trade of U.S. MNC's and of foreign MNC's is examined separately. This separation is warranted not only by the difference in the ownership of the investments (that is, whether it is U.S. or foreign) but also by a fundamental difference in the role that intrafirm trade has played in the operations of the MNC's: The intrafirm trade of U.S. MNC's has mainly been connected with manufacturing production by foreign affiliates, while the U.S. intrafirm trade of foreign MNC's has mainly been connected with marketing and distribution activities.
The following are highlights from the article:
The remainder of this article consists of three parts. The first part discusses trends in the shares of U.S. exports and imports of goods that are accounted for by intrafirm trade and in the shares accounted for by the intrafirm trade of U.S. MNC's and of foreign MNC's. The second part discusses industry patterns in the intrafirm trade of U.S. MNC's and foreign MNC's and examines the industry patterns of intrafirm trade of foreign MNC's by country of ultimate beneficial owner (UBO)./4/ The final part discusses the variation in intrafirm trade shares among U.S. trading partners and explores the relation between these shares and the per capita income levels of the partner countries.
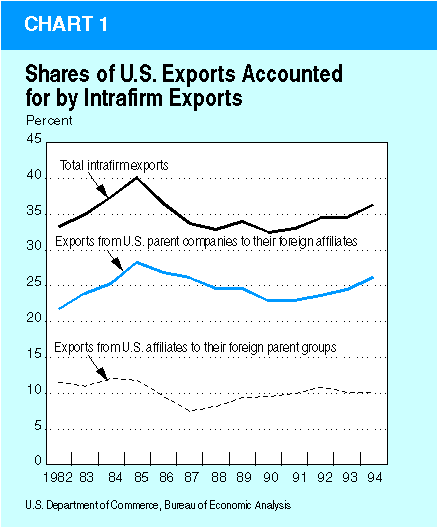
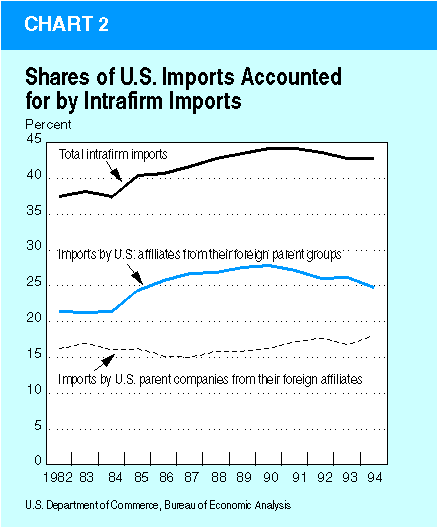
Although fluctuating moderately during the past two decades, the shares of intrafirm trade—both by U.S. MNC's and by foreign MNC's—in U.S. exports and imports of goods have changed very little. In 1977 (the earliest year for which trade data for both U.S. MNC's and foreign MNC's are available), intrafirm trade accounted for 35 percent of U.S. exports and 44 percent of U.S. imports. From 1982 to 1993, the share for exports fluctuated between 32 percent and 40 percent (chart 1); the share for imports—having dropped sharply between 1977 and 1982—increased in most years in the 1980's (chart 2). By 1994 (the latest year for which data are available), the share for exports had risen slightly, to 36 percent, while the share for imports had declined slightly, to 43 percent./5/
For both exports and imports, intrafirm trade has mainly consisted of shipments from parents to their affiliates rather than shipments to parents from their affiliates. U.S. intrafirm exports have mainly been accounted for by the intrafirm trade of U.S. MNC's—that is, shipments from U.S. parent companies to their foreign affiliates; the share in most years has ranged from two-thirds to three-fourths. Since 1982, U.S. intrafirm imports have mainly been accounted for by shipments from foreign parents and other member-firms of the foreign parent group to their U.S. affiliates./6/
The share of total U.S. goods exports that is accounted for by the intrafirm trade of U.S. MNC's has fluctuated between 22 percent and 28 percent. The share increased substantially in 1982–85, decreased gradually in the late 1980's, and then increased gradually after 1990./7/
The share of total U.S. goods imports that is accounted for by the intrafirm imports of U.S. MNC's has consistently been smaller than the corresponding share of exports. The share dropped sharply from 24 percent in 1977 to 16 percent in 1982; the drop can be largely attributed to a reduction in intrafirm imports from petroleum affiliates, partly as a result of transfers in the ownership of petroleum-producing assets in Middle Eastern countries to the host governments./8/ Since 1982, the import share has been quite stable (in the range of 15 to 18 percent).
 |
  |
| Because the U.S.-parent-company share of total U.S. goods trade has declined since the early 1980's (chart 3), the share of U.S. goods trade accounted for by intrafirm trade of U.S. MNC's has not increased substantially, even though the share of total goods trade by U.S. parent companies accounted for by intrafirm trade has increased markedly. | 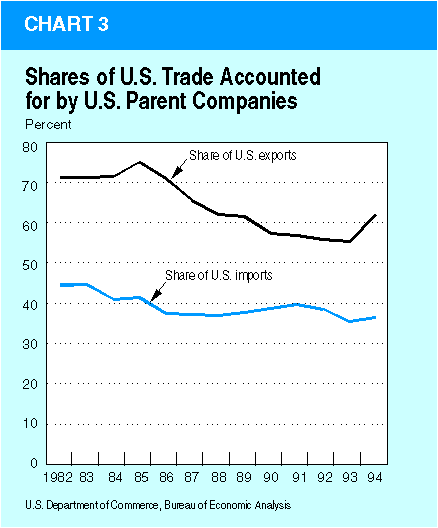 |
From 1982 to 1994, the share of U.S.-parent-company exports that were shipped to their foreign affiliates increased from 31 percent to 42 percent, while the share of U.S.-parent-company imports that were sourced from their foreign affiliates increased from 36 percent to 50 percent (chart 4). The share of U.S. goods exports accounted for by U.S. parent companies decreased substantially in the late 1980's (when the U.S. dollar was depreciating in world currency markets), perhaps as a result of an increased export orientation on the part of smaller U.S. firms in response to new market opportunities overseas. The share of U.S. goods imports accounted for by U.S. parent companies (which include most major U.S. petroleum companies) decreased in the early 1980's, when the share of total U.S. goods imports accounted for by petroleum imports declined as a result of a decline in oil prices.
| U.S. intrafirm exports of foreign MNC's have accounted for about 10
percent of total U.S. goods exports since 1977; the share has fluctuated between 7 percent
and 12 percent. In most years before 1986, the share exceeded 11 percent, primarily
reflecting the longstanding, dominant role played by Japanese-owned wholesale trade
affiliates (particularly affiliates of Japan's largest general trading companies) in
handling U.S. exports to Japan. (Japanese-owned affiliates accounted for most of the U.S.
intrafirm exports of foreign MNC's throughout 1977–94.) The share dropped below 10
percent in 1986–90, despite the surge in direct investment in the United States, and
it has hovered around 10 percent since then. The U.S. intrafirm imports of foreign MNC's have accounted for a much larger share of total U.S. goods imports—about 20 percent or more—since 1977. The share of imports increased substantially in 1984–90—from 21 percent to 28 percent—but has declined somewhat since. Like exports, a very large share of the U.S. intrafirm imports of foreign MNC's has been accounted for by Japanese-owned affiliates. |
 |
| Total | Millions of dollars | Percent | Addenda: | ||||||||||
| Total/1/ | Intrafirm trade | Other trade | Total | Intrafirm trade | Other trade | Intrafirm trade between U.S. parent companies and their foreign affiliates as a percentage of: |
Intrafirm trade of U.S. affiliates as a percentage of their total trade |
||||||
| Total | Between U.S. parent companies and their foreign affiliates |
Between U.S. affiliates and their foreign parent groups |
Total | Between U.S. parent companies and their foreign affiliates |
Between U.S. affiliates and their foreign parent groups |
Total trade of U.S. parents |
Total U.S. trade with foreign affiliates |
||||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) | (11) | (12) | (13) | |
| U.S. exports: | |||||||||||||
| 1977 | 123,182 | 43,010 | 31,319 | 11,691 | 80,172 | 100.0 | 34.9 | 25.4 | 9.5 | 65.1 | 33.9 | 76.8 | 47.0 |
| 1978 | 145,847 | n.a. | n.a. | 16,570 | n.a. | 100.0 | n.a. | n.a. | 11.4 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 51.5 |
| 1979 | 186,363 | n.a. | n.a. | 22,073 | n.a. | 100.0 | n.a. | n.a. | 11.8 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 49.8 |
| 1980 | 225,566 | n.a. | n.a. | 20,983 | n.a. | 100.0 | n.a. | n.a. | 9.3 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 40.2 |
| 1981 | 238,715 | n.a. | n.a. | 26,911 | n.a. | 100.0 | n.a. | n.a. | 11.3 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 42.0 |
| 1982 | 216,442 | 72,150 | 47,126 | 25,024 | 144,292 | 100.0 | 33.3 | 21.8 | 11.6 | 66.7 | 30.6 | 83.1 | 41.5 |
| 1983 | 205,639 | 71,974 | 49,397 | 22,577 | 133,665 | 100.0 | 35.0 | 24.0 | 11.0 | 65.0 | 33.8 | 85.8 | 41.9 |
| 1984 | 223,976 | 83,778 | 56,706 | 27,072 | 140,198 | 100.0 | 37.4 | 25.3 | 12.1 | 62.6 | 35.5 | 85.5 | 46.5 |
| 1985 | 218,815 | 87,752 | 61,852 | 25,900 | 131,063 | 100.0 | 40.1 | 28.3 | 11.8 | 59.9 | 37.7 | 88.8 | 45.9 |
| 1986 | 227,159 | 82,973 | 61,100 | 21,873 | 144,186 | 100.0 | 36.5 | 26.9 | 9.6 | 63.5 | 37.9 | 86.0 | 44.1 |
| 1987 | 254,122 | 85,523 | 66,414 | 19,109 | 168,599 | 100.0 | 33.7 | 26.1 | 7.5 | 66.3 | 39.9 | 84.2 | 39.7 |
| 1988 | 322,426 | 105,803 | 79,378 | 26,425 | 216,623 | 100.0 | 32.8 | 24.6 | 8.2 | 67.2 | 39.7 | 83.7 | 38.0 |
| 1989 | 363,812 | 123,714 | 89,438 | 34,276 | 240,098 | 100.0 | 34.0 | 24.6 | 9.4 | 66.0 | 40.1 | 87.2 | 39.7 |
| 1990 | 393,592 | 127,849 | 90,085 | 37,764 | 265,743 | 100.0 | 32.5 | 22.9 | 9.6 | 67.5 | 40.0 | 84.6 | 40.9 |
| 1991 | 421,730 | 139,346 | 97,124 | 42,222 | 282,384 | 100.0 | 33.0 | 23.0 | 10.0 | 67.0 | 40.5 | 84.2 | 43.6 |
| 1992 | 448,164 | 154,766 | 105,999 | 48,767 | 293,398 | 100.0 | 34.5 | 23.7 | 10.9 | 65.5 | 42.4 | 86.9 | 46.9 |
| 1993 | 465,091 | 161,112 | 113,762 | 47,350 | 303,979 | 100.0 | 34.6 | 24.5 | 10.2 | 65.4 | 44.3 | 86.4 | 44.4 |
| 1994 | 512,626 | 186,033 | 134,311 | 51,722 | 326,593 | 100.0 | 36.3 | 26.2 | 10.1 | 63.7 | 42.3 | 87.2 | 45.5 |
| U.S. imports: | |||||||||||||
| 1977 | 151,534 | 67,144 | 36,266 | 30,878 | 84,390 | 100.0 | 44.3 | 23.9 | 20.4 | 55.7 | 44.5 | 87.3 | 70.3 |
| 1978 | 176,052 | n.a. | n.a. | 39,466 | n.a. | 100.0 | n.a. | n.a. | 22.4 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 69.8 |
| 1979 | 210,285 | n.a. | n.a. | 45,295 | n.a. | 100.0 | n.a. | n.a. | 21.5 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 71.9 |
| 1980 | 245,262 | n.a. | n.a. | 47,010 | n.a. | 100.0 | n.a. | n.a. | 19.2 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 62.0 |
| 1981 | 260,982 | n.a. | n.a. | 52,196 | n.a. | 100.0 | n.a. | n.a. | 20.0 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 63.5 |
| 1982 | 243,952 | 91,203 | 39,288 | 51,915 | 152,749 | 100.0 | 37.4 | 16.1 | 21.3 | 62.6 | 36.2 | 76.4 | 61.6 |
| 1983 | 258,048 | 98,434 | 43,632 | 54,802 | 159,614 | 100.0 | 38.1 | 16.9 | 21.2 | 61.9 | 37.9 | 82.0 | 67.3 |
| 1984 | 330,678 | 123,244 | 52,793 | 70,451 | 207,434 | 100.0 | 37.3 | 16.0 | 21.3 | 62.7 | 38.9 | 83.8 | 70.1 |
| 1985 | 336,526 | 135,767 | 54,027 | 81,740 | 200,759 | 100.0 | 40.3 | 16.1 | 24.3 | 59.7 | 38.8 | 79.2 | 72.1 |
| 1986 | 365,438 | 148,430 | 55,012 | 93,418 | 217,008 | 100.0 | 40.6 | 15.1 | 25.6 | 59.4 | 40.2 | 84.0 | 74.3 |
| 1987 | 406,241 | 168,580 | 60,379 | 108,201 | 237,661 | 100.0 | 41.5 | 14.9 | 26.6 | 58.5 | 40.0 | 79.5 | 75.4 |
| 1988 | 440,952 | 187,853 | 69,491 | 118,362 | 253,099 | 100.0 | 42.6 | 15.8 | 26.8 | 57.4 | 42.6 | 79.6 | 76.1 |
| 1989 | 473,211 | 204,664 | 74,738 | 129,926 | 268,547 | 100.0 | 43.3 | 15.8 | 27.5 | 56.7 | 41.9 | 76.7 | 75.6 |
| 1990 | 495,310 | 217,757 | 80,299 | 137,458 | 277,553 | 100.0 | 44.0 | 16.2 | 27.8 | 56.0 | 41.9 | 78.6 | 75.1 |
| 1991 | 488,453 | 215,649 | 83,483 | 132,166 | 272,804 | 100.0 | 44.1 | 17.1 | 27.1 | 55.9 | 43.2 | 81.2 | 74.0 |
| 1992 | 532,665 | 231,692 | 93,893 | 137,799 | 300,973 | 100.0 | 43.5 | 17.6 | 25.9 | 56.5 | 45.8 | 86.7 | 74.7 |
| 1993 | 580,659 | 247,901 | 97,112 | 150,789 | 332,758 | 100.0 | 42.7 | 16.7 | 26.0 | 57.3 | 47.1 | 84.7 | 75.2 |
| 1994 | 663,256 | 283,504 | 119,438 | 164,066 | 379,752 | 100.0 | 42.7 | 18.0 | 24.7 | 57.3 | 49.6 | 91.8 | 74.9 |
n.a. Not available.
1. Data are from the Bureau of the Census.
The U.S. intrafirm trade of U.S. MNC's and the U.S. intrafirm trade of foreign MNC's have taken fundamentally different forms and have had quite different industry compositions. The intrafirm trade of U.S. MNC's can be viewed as an aspect of the international division of manufacturing production between affiliated parts of the MNC: For both exports and imports, most of this trade has been between U.S. manufacturing parents and their foreign manufacturing affiliates. The intrafirm exports to these manufacturing affiliates have mainly consisted of materials and components for further processing or assembly./9/ (Data on the intended use of U.S. imports from these foreign affiliates are not available.) In contrast, U.S. intrafirm trade of foreign MNC's has been connected largely with distribution and marketing activities: For both exports and imports, this trade has mainly been accounted for by U.S. wholesale trade affiliates. The imports by these affiliates from their foreign parent groups have consisted almost exclusively of goods for resale by the affiliates without further manufacture./10/ (Data on the intended use of exports by these affiliates are not available.)
The rest of this section presents added detail on the pattern of U.S. intrafirm trade associated with U.S. and foreign MNC's by industry of affiliate. In this section, the discussion of the intrafirm trade of U.S. MNC's is necessarily restricted to the intrafirm trade between U.S. parent companies and their majority-owned foreign affiliates (MOFA's); however, in the aggregate, intrafirm trade with MOFA's accounts for a very high share of U.S. intrafirm trade with all foreign affiliates./11/
Since 1982, MOFA's in manufacturing have consistently accounted for a dominant share of both U.S. intrafirm exports to MOFA's and U.S. intrafirm imports from MOFA's (table 2). The share of intrafirm exports to MOFA's that is accounted for by manufacturing affiliates has declined somewhat since the mid-1980's, when it exceeded 70 percent, while the share of exports to wholesale trade affiliates has increased. In contrast, the share of intrafirm imports from MOFA's that is accounted for by manufacturing affiliates has increased markedly—from less than 50 percent in 1977 to more than 80 percent in 1994—while the share of imports from petroleum affiliates has declined.
| Millions of dollars | Percent | Addendum: Intrafirm trade as a percentage of total U.S. trade with MOFA's | ||||||||||
| All industries | Manufacturing | Wholesale trade | Petroleum and other industries |
All industries | Manufacturing | Wholesale trade | Petroleum and other industries |
All industries | Manufacturing | Wholesale trade | Petroleum and other industries |
|
| Exports to MOFA's: | ||||||||||||
| 1977 | 29,275 | 20,510 | 6,607 | 2,158 | 100.0 | 70.1 | 22.6 | 7.4 | 81.7 | 81.6 | 86.6 | 71.1 |
| 1982 | 44,320 | 28,882 | 12,834 | 2,604 | 100.0 | 65.2 | 29.0 | 5.9 | 84.0 | 83.1 | 91.3 | 66.1 |
| 1983 | 45,107 | 31,304 | 11,588 | 2,215 | 100.0 | 69.4 | 25.7 | 4.9 | 82.8 | 83.4 | 88.6 | 57.8 |
| 1984 | 52,726 | 37,396 | 12,989 | 2,341 | 100.0 | 70.9 | 24.6 | 4.4 | 82.9 | 82.7 | 89.2 | 61.7 |
| 1985 | 57,567 | 40,513 | 14,640 | 2,414 | 100.0 | 70.4 | 25.4 | 4.2 | 86.6 | 86.0 | 92.9 | 66.5 |
| 1986 | 58,916 | 41,557 | 15,417 | 1,942 | 100.0 | 70.5 | 26.2 | 3.3 | 87.0 | 85.9 | 93.8 | 65.4 |
| 1987 | 65,248 | 45,516 | 17,559 | 2,173 | 100.0 | 69.8 | 26.9 | 3.3 | 87.1 | 85.8 | 94.8 | 65.6 |
| 1988 | 78,204 | 53,409 | 22,505 | 2,290 | 100.0 | 68.3 | 28.8 | 2.9 | 86.1 | 84.6 | 92.4 | 69.0 |
| 1989 | 86,050 | 57,707 | 25,247 | 3,096 | 100.0 | 67.1 | 29.3 | 3.6 | 88.3 | 86.8 | 94.2 | 73.7 |
| 1990 | 88,375 | 56,662 | 28,363 | 3,350 | 100.0 | 64.1 | 32.1 | 3.8 | 88.2 | 86.2 | 94.3 | 75.4 |
| 1991 | 95,779 | 62,915 | 29,128 | 3,736 | 100.0 | 65.7 | 30.4 | 3.9 | 88.0 | 86.2 | 94.0 | 76.8 |
| 1992 | 100,737 | 65,272 | 31,501 | 3,964 | 100.0 | 64.8 | 31.3 | 3.9 | 87.2 | 85.2 | 93.9 | 73.8 |
| 1993 | 106,827 | 66,051 | 37,091 | 3,685 | 100.0 | 61.8 | 34.7 | 3.4 | 86.1 | 82.5 | 94.6 | 75.9 |
| 1994 | 125,423 | 74,578 | 45,873 | 4,972 | 100.0 | 59.5 | 36.6 | 4.0 | 84.9 | 80.3 | 95.2 | 74.3 |
| Imports from MOFA's: | ||||||||||||
| 1977 | 30,880 | 14,492 | 1,322 | 15,066 | 100.0 | 46.9 | 4.3 | 48.8 | 81.3 | 82.1 | 78.6 | 80.7 |
| 1982 | 38,533 | 22,839 | 2,148 | 13,546 | 100.0 | 59.3 | 5.6 | 35.2 | 83.6 | 86.5 | 83.7 | 79.1 |
| 1983 | 41,551 | 27,584 | 2,679 | 11,288 | 100.0 | 66.4 | 6.4 | 27.2 | 86.0 | 88.1 | 87.2 | 80.9 |
| 1984 | 49,316 | 34,388 | 3,302 | 11,626 | 100.0 | 69.7 | 6.7 | 23.6 | 85.7 | 88.6 | 88.2 | 77.7 |
| 1985 | 51,751 | 36,687 | 3,433 | 11,631 | 100.0 | 70.9 | 6.6 | 22.5 | 85.8 | 88.7 | 78.0 | 80.0 |
| 1986 | 49,961 | 38,912 | 4,292 | 6,757 | 100.0 | 77.9 | 8.6 | 13.5 | 87.2 | 88.9 | 89.6 | 77.5 |
| 1987 | 55,867 | 41,492 | 5,629 | 8,746 | 100.0 | 74.3 | 10.1 | 15.7 | 85.2 | 87.5 | 85.9 | 75.7 |
| 1988 | 65,464 | 51,404 | 6,491 | 7,569 | 100.0 | 78.5 | 9.9 | 11.6 | 86.6 | 89.0 | 90.0 | 71.2 |
| 1989 | 71,283 | 57,070 | 6,069 | 8,144 | 100.0 | 80.1 | 8.5 | 11.4 | 84.6 | 87.6 | 80.4 | 70.3 |
| 1990 | 75,251 | 59,427 | 5,895 | 9,929 | 100.0 | 79.0 | 7.8 | 13.2 | 84.9 | 86.9 | 82.2 | 75.7 |
| 1991 | 77,578 | 60,448 | 7,178 | 9,952 | 100.0 | 77.9 | 9.3 | 12.8 | 85.7 | 87.9 | 82.9 | 76.0 |
| 1992 | 83,260 | 67,241 | 7,803 | 8,216 | 100.0 | 80.8 | 9.4 | 9.9 | 86.6 | 88.8 | 88.7 | 72.4 |
| 1993 | 93,205 | 76,579 | 8,677 | 7,949 | 100.0 | 82.2 | 9.3 | 8.5 | 86.3 | 89.0 | 89.4 | 65.0 |
| 1994 | 103,502 | 85,762 | 10,173 | 7,567 | 100.0 | 82.9 | 9.8 | 7.3 | 87.6 | 90.9 | 88.9 | 61.4 |
MOFA Majority-owned foreign affiliate
Much of the intrafirm trade with manufacturing affiliates has consisted of trade with motor vehicle affiliates: In 1982–94, the share of total intrafirm trade with manufacturing MOFA's that was accounted for by motor vehicle affiliates ranged from 38 to 48 percent for exports and from 44 to 54 percent for imports. Much of this trade was with affiliates in Canada, reflecting the large volume of auto-related trade since the U.S.-Canada Automobile Agreement of 1965. Intrafirm trade with affiliates in machinery industries (industrial and electronic and other electric machinery manufacturing) has also been substantial, accounting for 27 to 32 percent of intrafirm exports to, and for 30 to 37 percent of intrafirm imports from, manufacturing MOFA's.
The share of intrafirm exports that was to MOFA's in wholesale trade increased substantially in 1984–94—from 25 percent to 37 percent. Much of this trade was in machinery products./12/
In 1977, petroleum affiliates accounted for 49 percent of total intrafirm imports from MOFA's; however, by 1982, their share had dropped to 35 percent, partly as a result of the transfers in the ownership of petroleum-producing assets in Middle Eastern countries to host governments. The share continued to decline in 1982–86, reflecting a fall in the U.S.-import price of crude oil.
Unlike the intrafirm trade of U.S. MNC's, which has been dominated by trade with manufacturing affiliates, the intrafirm trade of foreign MNC's—between U.S. affiliates and their foreign parent groups—has been mostly with wholesale trade affiliates. Through the mid-1980's, these affiliates accounted for more than three-fourths of the intrafirm exports and imports of foreign-owned U.S. affiliates; in more recent years, the share has been closer to two-thirds (table 3).
| Millions of dollars | Percent | Addendum: Intrafirm trade of U.S. affiliates as a percentage of their total trade | ||||||||||
| All industries | Manufacturing | Wholesale trade | Petroleum and other industries |
All industries | Manufacturing | Wholesale trade | Petroleum and other industries |
All industries | Manufacturing | Wholesale trade | Petroleum and other industries |
|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) | (11) | (12) | |
| Exports to foreign parent groups: |
||||||||||||
| 1977 | 11,691 | 1,365 | 9,588 | 738 | 100.0 | 11.7 | 82.0 | 6.3 | 47.0 | 38.4 | 48.0 | 56.0 |
| 1978 | 16,570 | 1,597 | 13,977 | 996 | 100.0 | 9.6 | 84.4 | 6.0 | 51.5 | 35.3 | 54.0 | 56.9 |
| 1979 | 22,073 | 2,019 | 18,761 | 1,293 | 100.0 | 9.1 | 85.0 | 5.9 | 49.8 | 30.8 | 52.7 | 59.0 |
| 1980 | 20,983 | 2,643 | 17,258 | 1,082 | 100.0 | 12.6 | 82.2 | 5.2 | 40.2 | 29.2 | 42.4 | 44.4 |
| 1981 | 26,911 | 2,945 | 22,416 | 1,550 | 100.0 | 10.9 | 83.3 | 5.8 | 42.0 | 21.7 | 48.2 | 38.9 |
| 1982 | 25,024 | 3,112 | 20,341 | 1,571 | 100.0 | 12.4 | 81.3 | 6.3 | 41.5 | 24.2 | 46.9 | 39.1 |
| 1983 | 22,577 | 3,108 | 18,033 | 1,436 | 100.0 | 13.8 | 79.9 | 6.4 | 41.9 | 25.8 | 46.9 | 42.8 |
| 1984 | 27,072 | 3,713 | 22,117 | 1,242 | 100.0 | 13.7 | 81.7 | 4.6 | 46.5 | 28.4 | 54.6 | 27.2 |
| 1985 | 25,900 | 3,671 | 20,768 | 1,461 | 100.0 | 14.2 | 80.2 | 5.6 | 45.9 | 28.6 | 54.3 | 27.6 |
| 1986 | 21,873 | 3,894 | 16,661 | 1,318 | 100.0 | 17.8 | 76.2 | 6.0 | 44.1 | 30.4 | 49.4 | 43.5 |
| 1987 | 19,109 | 4,491 | 13,370 | 1,248 | 100.0 | 23.5 | 70.0 | 6.5 | 39.7 | 29.0 | 45.8 | 36.3 |
| 1988 | 26,425 | 6,544 | 18,257 | 1,624 | 100.0 | 24.8 | 69.1 | 6.1 | 38.0 | 26.0 | 45.6 | 37.6 |
| 1989 | 34,276 | 7,926 | 24,782 | 1,568 | 100.0 | 23.1 | 72.3 | 4.6 | 39.7 | 24.9 | 50.5 | 29.3 |
| 1990 | 37,764 | 9,067 | 26,636 | 2,061 | 100.0 | 24.0 | 70.5 | 5.5 | 40.9 | 25.1 | 53.4 | 32.6 |
| 1991 | 42,222 | 10,445 | 28,887 | 2,890 | 100.0 | 24.7 | 68.4 | 6.8 | 43.6 | 27.7 | 55.2 | 41.8 |
| 1992 | 48,767 | 11,574 | 34,612 | 2,581 | 100.0 | 23.7 | 71.0 | 5.3 | 46.9 | 28.7 | 62.2 | 32.4 |
| 1993 | 47,350 | 12,092 | 33,336 | 1,922 | 100.0 | 25.5 | 70.4 | 4.1 | 44.4 | 27.8 | 59.5 | 26.7 |
| 1994 | 51,722 | 13,827 | 35,513 | 2,382 | 100.0 | 26.7 | 68.7 | 4.6 | 45.5 | 28.6 | 62.2 | 28.7 |
| Imports from foreign parent groups: |
||||||||||||
| 1977 | 30,878 | 4,512 | 23,791 | 2,575 | 100.0 | 14.6 | 77.0 | 8.3 | 70.3 | 80.2 | 75.8 | 37.3 |
| 1978 | 39,466 | 5,761 | 31,453 | 2,252 | 100.0 | 14.6 | 79.7 | 5.7 | 69.8 | 80.1 | 73.6 | 33.9 |
| 1979 | 45,295 | 6,444 | 36,082 | 2,769 | 100.0 | 14.2 | 79.7 | 6.1 | 71.9 | 74.3 | 79.1 | 31.6 |
| 1980 | 47,010 | 7,808 | 36,068 | 3,134 | 100.0 | 16.6 | 76.7 | 6.7 | 62.0 | 75.0 | 66.8 | 27.6 |
| 1981 | 52,196 | 8,019 | 41,981 | 2,196 | 100.0 | 15.4 | 80.4 | 4.2 | 63.5 | 60.6 | 72.5 | 19.7 |
| 1982 | 51,915 | 7,680 | 41,083 | 3,152 | 100.0 | 14.8 | 79.1 | 6.1 | 61.6 | 62.0 | 66.6 | 30.8 |
| 1983 | 54,802 | 9,202 | 43,208 | 2,392 | 100.0 | 16.8 | 78.8 | 4.4 | 67.3 | 65.6 | 73.2 | 28.5 |
| 1984 | 70,451 | 11,397 | 57,071 | 1,983 | 100.0 | 16.2 | 81.0 | 2.8 | 70.1 | 62.7 | 78.7 | 20.2 |
| 1985 | 81,740 | 12,432 | 66,898 | 2,410 | 100.0 | 15.2 | 81.8 | 2.9 | 72.1 | 66.7 | 79.1 | 23.8 |
| 1986 | 93,418 | 14,626 | 75,498 | 3,294 | 100.0 | 15.7 | 80.8 | 3.5 | 74.3 | 70.9 | 79.9 | 31.1 |
| 1987 | 108,201 | 17,570 | 85,092 | 5,539 | 100.0 | 16.2 | 78.6 | 5.1 | 75.4 | 71.6 | 79.3 | 47.3 |
| 1988 | 118,362 | 21,952 | 90,649 | 5,761 | 100.0 | 18.5 | 76.6 | 4.9 | 76.1 | 67.0 | 81.3 | 51.0 |
| 1989 | 129,926 | 27,587 | 93,243 | 9,096 | 100.0 | 21.2 | 71.8 | 7.0 | 75.6 | 67.5 | 81.8 | 53.7 |
| 1990 | 137,458 | 33,221 | 91,441 | 12,796 | 100.0 | 24.2 | 66.5 | 9.3 | 75.1 | 70.4 | 80.5 | 57.8 |
| 1991 | 132,166 | 32,730 | 88,289 | 11,147 | 100.0 | 24.8 | 66.8 | 8.4 | 74.0 | 69.6 | 78.9 | 56.2 |
| 1992 | 137,799 | 37,259 | 89,202 | 11,338 | 100.0 | 27.0 | 64.7 | 8.2 | 74.7 | 69.9 | 81.4 | 52.8 |
| 1993 | 150,789 | 39,866 | 99,649 | 11,274 | 100.0 | 26.4 | 66.1 | 7.5 | 75.2 | 66.9 | 83.2 | 52.8 |
| 1994 | 164,066 | 45,105 | 109,634 | 9,327 | 100.0 | 27.5 | 66.8 | 5.7 | 74.9 | 67.3 | 83.5 | 44.6 |
Until recently, the intrafirm exports by wholesale trade affiliates largely consisted of homogeneous commodities—such as food and crude materials—shipped by affiliates of Japan's general trading companies or by French-owned affiliates specializing in farm products./13/ The share of the intrafirm exports of wholesale trade affiliates that was accounted for by food and crude materials was 59 percent in 1980 and 50 percent in 1987 (table 4). By 1992, however, this share had declined to 41 percent, reflecting an increase in the importance of manufactured goods in intrafirm exports.
| Millions of dollars | Percent | |||||
| 1980 | 1987 | 1992 | 1980 | 1987 | 1992 | |
| Exports, total | 17,258 | 13,370 | 34,612 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Food | 6,246 | 3,708 | 8,772 | 36.2 | 27.7 | 25.3 |
| Crude materials, inedible, except fuels | 3,910 | 3,029 | 5,280 | 22.7 | 22.7 | 15.3 |
| Chemicals | 953 | 1,057 | 2,422 | 5.5 | 7.9 | 7.0 |
| Machinery | 1,436 | 1,676 | 5,745 | 8.3 | 12.5 | 16.6 |
| Road vehicles and parts | 203 | 236 | 2,156 | 1.2 | 1.8 | 6.2 |
| Other transport equipment | 397 | (/D/) | 2,698 | 2.3 | (/D/) | 7.8 |
| Metal manufactures | 1,068 | 734 | 1,463 | 6.2 | 5.5 | 4.2 |
| Other | 3,045 | (/D/) | 6,076 | 17.6 | (/D/) | 17.6 |
| Imports, total | 36,068 | 85,092 | 89,202 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Food | 1,692 | 1,888 | 1,532 | 4.7 | 2.2 | 1.7 |
| Crude materials, inedible, except fuels | 836 | 1,526 | 2,059 | 2.3 | 1.8 | 2.3 |
| Chemicals | 827 | 1,403 | 2,595 | 2.3 | 1.6 | 2.9 |
| Machinery | 7,606 | 25,526 | 33,489 | 21.1 | 30.0 | 37.5 |
| Road vehicles and parts | (/D/) | 39,340 | 27,639 | (/D/) | 46.2 | 31.0 |
| Other transport equipment | 511 | 396 | 1,960 | 1.4 | 0.5 | 2.2 |
| Metal manufactures | 5,682 | 4,607 | 4,891 | 15.8 | 5.4 | 5.5 |
| Other | (/D/) | 10,406 | 15,037 | (/D/) | 12.2 | 16.9 |
D Suppressed to avoid the disclosure of data of individual companies.
In contrast, the intrafirm imports of wholesale trade affiliates have mainly consisted of heterogeneous manufactured products, such as machinery products or road vehicles and parts. For such products, a local presence in the form of wholesale trade affiliates may be required to provide specialized after-sales service or to obtain continuous feedback on customer requirements and tastes. Most of these affiliates were set up by foreign manufacturers to facilitate the marketing of their own products; in most years, intrafirm imports from their foreign parents have accounted for more than three-fourths of the total imports by these affiliates (table 3, column 11).
The shares of U.S.-affiliate intrafirm exports and imports accounted for by manufacturing affiliates have increased substantially. For exports, the share increased gradually from 12 percent in 1977 to 27 percent in 1994. For imports, the increase largely coincided with the surge in foreign direct investment in U.S. manufacturing industries in the mid-to-late 1980's; the share increased from 15 percent in 1985 to 27 percent in 1992./14/
Within manufacturing, the industry composition of intrafirm trade with U.S. affiliates has been somewhat more diversified than that of intrafirm trade with MOFA's; however, affiliates in chemicals and in electronic and other electric equipment have generally accounted for the largest shares of intrafirm exports and imports by U.S. manufacturing affiliates./15/
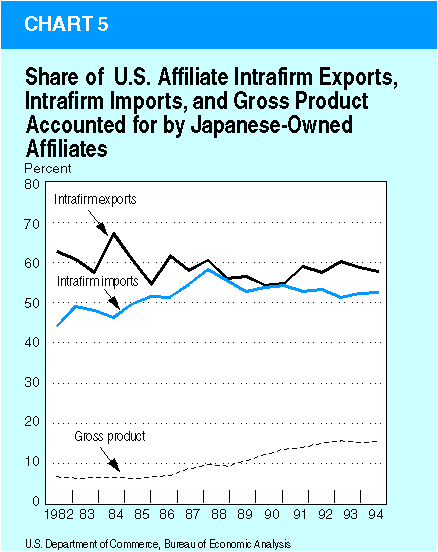
By country of UBO.—Since 1977, affiliates with UBO's in Japan have accounted for a dominant share of U.S.-affiliate intrafirm exports: The share has fluctuated in the range of 55 to 68 percent—many times larger than their share of U.S.-affiliate gross product (chart 5). Since 1982, Japanese-owned affiliates have also accounted for more than one-half of U.S.-affiliate intrafirm imports. For both exports and imports, this dominance mainly reflects trade by Japanese-owned wholesale trade affiliates, which function as intermediate agents for much of Japan's trade with the United States.
| Within wholesale trade, Japanese-owned affiliates have accounted for
about three-fourths of U.S.-affiliate intrafirm exports and for nearly two-thirds of
U.S.-affiliate intrafirm imports (table 5). French-owned affiliates, mainly farm-product
trading companies, have generally accounted for the second-largest share of the intrafirm
exports; German-owned affiliates, mainly wholesale trade affiliates of motor vehicle
manufacturers, have generally accounted for the second-largest share of the intrafirm
imports. In manufacturing, the shares of the intrafirm trade of affiliates have been much more evenly distributed among investing countries. Japanese-owned affiliates accounted for the largest shares of both intrafirm exports and imports in 1994, but their share of exports was less than one-fourth, and their share of imports was less than one-third. German-owned affiliates accounted for the second-largest shares—about one-sixth of both exports and imports. In the 1980's, the shares of Japanese-owned affiliates were substantially smaller: In 1984, their share of exports was exceeded by the shares of German-, British-, and Canadian-owned affiliates, and their share of imports was exceeded by the shares of Canadian- and German-owned affiliates. The increased share of Japanese-owned affiliates after 1984 reflects the large increase in Japanese ownership in U.S. manufacturing industries in the late 1980's./16/ |
 |
| Millions of dollars | Percent of all-countries total | |||||||||||||||
| Exports to foreign parent groups | Imports from foreign parent groups | Exports | Imports | |||||||||||||
| 1984 | 1988 | 1992 | 1994 | 1984 | 1988 | 1992 | 1994 | 1984 | 1988 | 1992 | 1994 | 1984 | 1988 | 1992 | 1994 | |
| All industries: | ||||||||||||||||
| All countries | 27,072 | 26,425 | 48,767 | 51,722 | 70,451 | 118,362 | 137,799 | 164,066 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Canada | 881 | 1,109 | 1,569 | 1,835 | 4,844 | 6,899 | 7,125 | 8,237 | 3.3 | 4.2 | 3.2 | 3.5 | 6.9 | 5.8 | 5.2 | 5.0 |
| France | 4,367 | 1,283 | 4,219 | 5,140 | 2,801 | 4,486 | 4,673 | 5,368 | 16.1 | 4.9 | 8.7 | 9.9 | 4.0 | 3.8 | 3.4 | 3.3 |
| Germany | 1,050 | 1,795 | 2,471 | 2,778 | 9,324 | 13,835 | 15,422 | 18,840 | 3.9 | 6.8 | 5.1 | 5.4 | 13.2 | 11.7 | 11.2 | 11.5 |
| Netherlands | 765 | 1,405 | 1,546 | 1,773 | 1,314 | 2,237 | 4,297 | 4,095 | 2.8 | 5.3 | 3.2 | 3.4 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 3.1 | 2.5 |
| Sweden | 176 | 289 | 404 | 791 | 2,581 | 4,168 | 3,798 | 4,288 | .7 | 1.1 | .8 | 1.5 | 3.7 | 3.5 | 2.8 | 2.6 |
| Switzerland | 771 | 757 | 1,417 | 1,850 | 1,507 | 3,829 | 3,877 | 4,830 | 2.8 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 3.6 | 2.1 | 3.2 | 2.8 | 2.9 |
| United Kingdom | 854 | 1,291 | 2,170 | 2,051 | 3,479 | 5,594 | 6,804 | 7,446 | 3.2 | 4.9 | 4.4 | 4.0 | 4.9 | 4.7 | 4.9 | 4.5 |
| Japan | 15,775 | 14,463 | 29,551 | 30,049 | 38,688 | 63,903 | 71,152 | 86,674 | 58.3 | 54.7 | 60.6 | 58.1 | 54.9 | 54.0 | 51.6 | 52.8 |
| Korea, Republic of | 555 | 1,400 | 1,305 | 1,271 | 1,387 | 4,542 | 3,857 | 6,563 | 2.0 | 5.3 | 2.7 | 2.5 | 2.0 | 3.8 | 2.8 | 4.0 |
| Other countries | 1,877 | 2,634 | 4,115 | 4,184 | 4,525 | 8,869 | 16,794 | 17,725 | 6.9 | 10.0 | 8.4 | 8.1 | 6.4 | 7.5 | 12.2 | 10.8 |
| Manufacturing: | ||||||||||||||||
| All countries | 3,713 | 6,544 | 11,574 | 13,827 | 11,397 | 21,952 | 37,259 | 45,105 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Canada | 434 | 503 | 1,055 | 1,345 | 2,285 | 2,962 | 3,706 | 4,670 | 11.7 | 7.7 | 9.1 | 9.7 | 20.0 | 13.5 | 9.9 | 10.4 |
| France | 150 | 527 | 1,014 | (/D/) | 1,185 | 2,107 | 2,427 | 2,806 | 4.0 | 8.1 | 8.8 | (/D/) | 10.4 | 9.6 | 6.5 | 6.2 |
| Germany | 674 | 1,420 | 1,934 | 2,297 | 2,169 | 4,034 | 6,513 | 7,192 | 18.2 | 21.7 | 16.7 | 16.6 | 19.0 | 18.4 | 17.5 | 15.9 |
| Netherlands | 300 | 876 | 911 | 961 | 721 | 1,167 | 1,734 | 1,961 | 8.1 | 13.4 | 7.9 | 7.0 | 6.3 | 5.3 | 4.7 | 4.3 |
| Sweden | 86 | 251 | 315 | 738 | 439 | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | 2.3 | 3.8 | 2.7 | 5.3 | 3.9 | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) |
| Switzerland | 290 | 425 | 1,131 | 1,585 | 780 | 1,866 | 2,532 | 3,043 | 7.8 | 6.5 | 9.8 | 11.5 | 6.8 | 8.5 | 6.8 | 6.7 |
| United Kingdom | 532 | 1,060 | 1,466 | 1,597 | 1,230 | 2,186 | 3,883 | 4,945 | 14.3 | 16.2 | 12.7 | 11.5 | 10.8 | 10.0 | 10.4 | 11.0 |
| Japan | 364 | 786 | 2,731 | 3,184 | 1,327 | 5,144 | 12,315 | 14,488 | 9.8 | 12.0 | 23.6 | 23.0 | 11.6 | 23.4 | 33.1 | 32.1 |
| Korea, Republic of | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | 46 | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | .4 | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) |
| Other countries | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | 1,129 | 1,216 | 1,680 | 2,910 | 4,092 | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | 8.2 | 10.7 | 7.7 | 7.8 | 9.1 |
| Wholesale trade: | ||||||||||||||||
| All countries | 22,117 | 18,257 | 34,612 | 35,513 | 57,071 | 90,649 | 89,202 | 109,634 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Canada | 115 | 118 | 282 | 384 | 2,002 | 3,178 | 2,412 | 2,345 | .5 | .6 | .8 | 1.1 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 2.7 | 2.1 |
| France | (/D/) | 745 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 1,600 | 2,287 | 1,994 | 2,387 | (/D/) | 4.1 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 2.8 | 2.5 | 2.2 | 2.2 |
| Germany | 351 | 347 | 481 | 440 | 7,116 | 9,749 | 8,694 | 11,434 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 12.5 | 10.8 | 9.7 | 10.4 |
| Netherlands | 64 | (/D/) | 83 | 176 | 176 | 385 | 1,520 | 1,521 | .3 | (/D/) | .2 | .5 | .3 | .4 | 1.7 | 1.4 |
| Sweden | (/D/) | (/D/) | 87 | (/D/) | 2,125 | 3,457 | 2,940 | 2,806 | (/D/) | (/D/) | .3 | (/D/) | 3.7 | 3.8 | 3.3 | 2.6 |
| Switzerland | (/D/) | 259 | 159 | 156 | 719 | 1,363 | 1,226 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 1.4 | .5 | .4 | 1.3 | 1.5 | 1.4 | (/D/) |
| United Kingdom | 123 | 150 | 466 | 270 | 1,973 | 2,574 | 2,330 | 2,030 | .6 | .8 | 1.3 | .8 | 3.5 | 2.8 | 2.6 | 1.9 |
| Japan | 15,314 | 13,572 | 26,533 | 26,714 | 37,140 | 58,617 | 58,684 | 72,038 | 69.2 | 74.3 | 76.7 | 75.2 | 65.1 | 64.7 | 65.8 | 65.7 |
| Korea, Republic of | 551 | 1,084 | 1,263 | 989 | 1,342 | 4,199 | 3,444 | 5,765 | 2.5 | 5.9 | 3.7 | 2.8 | 2.4 | 4.6 | 3.9 | 5.3 |
| Other countries | 840 | 1,723 | (/D/) | 2,174 | 2,879 | 4,838 | 5,958 | (/D/) | 3.8 | 9.4 | (/D/) | 6.1 | 5.0 | 5.3 | 6.7 | (/D/) |
| Petroleum and other industries: | ||||||||||||||||
| All countries | 1,242 | 1,624 | 2,581 | 2,382 | 1,983 | 5,761 | 11,338 | 9,327 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Canada | 332 | 488 | 232 | 106 | 557 | 759 | 1,007 | 1,222 | 26.7 | 30.1 | 9.0 | 4.5 | 28.1 | 13.2 | 8.9 | 13.1 |
| France | (/D/) | 11 | (/D/) | 14 | 16 | 92 | 252 | 175 | (/D/) | .7 | (/D/) | .6 | .8 | 1.6 | 2.2 | 1.9 |
| Germany | 25 | 28 | 56 | 41 | 39 | 52 | 215 | 214 | 2.0 | 1.7 | 2.2 | 1.7 | 2.0 | .9 | 1.9 | 2.3 |
| Netherlands | 401 | (/D/) | 552 | 636 | 417 | 685 | 1,043 | 613 | 32.3 | (/D/) | 21.4 | 26.7 | 21.0 | 11.9 | 9.2 | 6.6 |
| Sweden | (/D/) | (/D/) | 2 | (/D/) | 17 | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | .1 | (/D/) | .9 | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) |
| Switzerland | (/D/) | 73 | 127 | 109 | 9 | 600 | 119 | 336 | (/D/) | 4.5 | 4.9 | 4.6 | .5 | 10.4 | 1.0 | (/D/) |
| United Kingdom | 198 | 81 | 238 | 184 | 276 | 835 | 591 | 471 | 16.0 | 5.0 | 9.2 | 7.7 | 13.9 | 14.5 | 5.2 | 5.0 |
| Japan | 97 | 105 | 287 | 151 | 222 | 142 | 153 | 148 | 7.8 | 6.5 | 11.1 | 6.3 | 11.2 | 2.5 | 1.3 | 1.6 |
| Korea, Republic of | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | (*) | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | (*) | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) |
| Other countries | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | 880 | 430 | 2,350 | 7,926 | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | 37.0 | 21.7 | 40.8 | 69.9 | (/D/) |
D Suppressed to the avoid disclosure of data of individual companies.
* Less than $500,000 or less than .05 percent, as appropriate.
UBO Ultimate beneficial owner
The importance of intrafirm trade in total U.S. international trade in goods varies widely by trading partner. This section examines the shares of total U.S. trade in goods with major trading-partner countries that are accounted for by total intrafirm trade, by intrafirm trade between U.S. parent companies and MOFA's, and by intrafirm trade between U.S. affiliates and their foreign parent groups. The shares are computed for 1992, the most recent year for which geographic data on U.S.-affiliate intrafirm trade are available./17/
The presentation is in two parts. The first part discusses differences in the intrafirm-trade shares for trade with 62 major partner countries, and the second explores the relation between these shares and the income levels of the partner countries./18/
Exports.—In 1992, the share of U.S. exports accounted for by intrafirm exports varied widely across countries of destination. For example, among the top six U.S. export markets—Canada, Japan, Mexico, the United Kingdom, Germany, and Taiwan—the intrafirm share ranged from 70 percent for Japan to 12 percent for Taiwan (chart 6 and table 6, column 7). In addition, the intrafirm-trade shares were particularly high for Switzerland (74 percent) and Russia (64 percent). For 24 of the 62 countries, the intrafirm share was less than 10 percent.
| For most countries, U.S. intrafirm exports consisted mainly of exports by
U.S. parent companies to their MOFA's rather than exports by U.S. affiliates to their
foreign parent groups. Intrafirm exports to MOFA's accounted for more than 20 percent of
total U.S. exports to 13 countries, many of which were among the largest U.S. export
markets (table 6, column 8). The shares were highest for Switzerland (56 percent), Canada
(37 percent), and the United Kingdom (34 percent). The intrafirm exports to MOFA's in
Switzerland were mainly shipped to wholesale trade affiliates (table 7). Exports to
manufacturing affiliates accounted for a dominant share of intrafirm exports to MOFA's in
most other countries, including Canada and the United Kingdom. For all but a few countries, the share of U.S. exports accounted for by intrafirm exports by foreign-owned U.S. affiliates was small—less than 10 percent (table 6, column 9). However, for Japan, the second largest U.S. export market in 1992, the share was 54 percent. The large share for Japan underscores the importance of wholesale trade affiliates in handling Japanese trade with the United States: About 90 percent of total U.S.-affiliate intrafirm exports to Japan was accounted for by Japanese-owned wholesale trade affiliates (table 8). Intrafirm exports by U.S. affiliates also accounted for a majority of U.S. exports to Russia and for about one-fourth of U.S. exports to Nigeria; however, these exports were all shipped by affiliates with owners in other countries./19/ The exports to Russia were mainly by French-owned wholesale trade affiliates, and the exports to Nigeria were mainly by European-owned affiliates in the petroleum industry./20/ |
 |
| Exports by country of destination | Imports by country of origin | |||||||||||||||||||
| Millions of dollars | Percent | Millions of dollars | Percent | |||||||||||||||||
| Total/1/ | Intrafirm exports | Other exports | Total | Intrafirm exports | Other exports | Total/1/ | Intrafirm imports | Other imports | Total | Intrafirm imports | Other imports | |||||||||
| Total | By U.S. parent companies to their majority-owned foreign affiliates |
By U.S. affiliates to their foreign parent groups |
Total | By U.S. parent companies to their majority-owned foreign affiliates |
By U.S. affiliates to their foreign parent groups |
Total | By U.S. parent companies from their majority-owned foreign affiliates |
By U.S. affiliates from their foreign parent groups |
Total | By U.S. parent companies from their majority-owned foreign affiliates |
By U.S. affiliates from their foreign parent groups |
|||||||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) | (11) | (12) | (13) | (14) | (15) | (16) | (17) | (18) | (19) | (20) | |
| All countries | 448,164 | 149,504 | 100,737 | 48,767 | 298,660 | 100.0 | 33.4 | 22.5 | 10.9 | 66.6 | 532,665 | 221,059 | 83,260 | 137,799 | 311,606 | 100.0 | 41.5 | 15.6 | 25.9 | 58.5 |
| Canada | 90,594 | 37,484 | 33,878 | 3,606 | 53,110 | 100.0 | 41.4 | 37.4 | 4.0 | 58.6 | 98,630 | 46,061 | 36,613 | 9,448 | 52,569 | 100.0 | 46.7 | 37.1 | 9.6 | 53.3 |
| Europe | 122,617 | 43,500 | 32,829 | 10,671 | 79,117 | 100.0 | 35.5 | 26.8 | 8.7 | 64.5 | 112,707 | 52,226 | 12,967 | 39,259 | 60,481 | 100.0 | 46.3 | 11.5 | 34.8 | 53.7 |
| Austria | 1,256 | 313 | 223 | 90 | 943 | 100.0 | 24.9 | 17.8 | 7.2 | 75.1 | 1,307 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 415 | (/D/) | 100.0 | B | A | 31.8 | E |
| Belgium and Luxembourg | 10,047 | 3,053 | 2,598 | 455 | 6,994 | 100.0 | 30.4 | 25.9 | 4.5 | 69.6 | 4,703 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 1,767 | (/D/) | 100.0 | C | A | 37.6 | C |
| Denmark | 1,473 | 194 | 160 | 34 | 1,279 | 100.0 | 13.2 | 10.9 | 2.3 | 86.8 | 1,667 | 565 | 68 | 497 | 1,102 | 100.0 | 33.9 | 4.1 | 29.8 | 66.1 |
| Finland | 785 | 142 | 74 | 68 | 643 | 100.0 | 18.1 | 9.4 | 8.7 | 81.9 | 1,185 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 354 | (/D/) | 100.0 | B | A | 29.9 | E |
| France | 14,593 | 4,947 | 3,975 | 972 | 9,646 | 100.0 | 33.9 | 27.2 | 6.7 | 66.1 | 14,797 | 5,717 | 1,829 | 3,888 | 9,080 | 100.0 | 38.6 | 12.4 | 26.3 | 61.4 |
| Germany | 21,249 | 8,446 | 6,544 | 1,902 | 12,803 | 100.0 | 39.7 | 30.8 | 9.0 | 60.3 | 28,820 | 17,438 | 2,558 | 14,880 | 11,382 | 100.0 | 60.5 | 8.9 | 51.6 | 39.5 |
| Greece | 901 | 32 | 26 | 6 | 869 | 100.0 | 3.6 | 2.9 | .7 | 96.4 | 370 | (/D/) | 2 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | .5 | A | F |
| Ireland | 2,862 | 887 | 834 | 53 | 1,975 | 100.0 | 31.0 | 29.1 | 1.9 | 69.0 | 2,262 | 1,255 | 1,053 | 202 | 1,007 | 100.0 | 55.5 | 46.6 | 8.9 | 44.5 |
| Italy | 8,721 | 2,060 | 1,614 | 446 | 6,661 | 100.0 | 23.6 | 18.5 | 5.1 | 76.4 | 12,314 | 1,907 | 616 | 1,291 | 10,407 | 100.0 | 15.5 | 5.0 | 10.5 | 84.5 |
| Netherlands | 13,752 | 5,212 | 4,412 | 800 | 8,540 | 100.0 | 37.9 | 32.1 | 5.8 | 62.1 | 5,300 | 3,421 | 891 | 2,530 | 1,879 | 100.0 | 64.5 | 16.8 | 47.7 | 35.5 |
| Norway | 1,279 | 209 | 124 | 85 | 1,070 | 100.0 | 16.3 | 9.7 | 6.6 | 83.7 | 1,969 | 402 | 129 | 273 | 1,567 | 100.0 | 20.4 | 6.6 | 13.9 | 79.6 |
| Poland | 641 | 12 | (*) | 12 | 629 | 100.0 | 1.9 | (*) | 1.9 | 98.1 | 375 | 20 | 0 | 20 | 355 | 100.0 | 5.3 | 0 | 5.3 | 94.7 |
| Portugal | 1,025 | 141 | 111 | 30 | 884 | 100.0 | 13.8 | 10.8 | 2.9 | 86.2 | 664 | 33 | 26 | 7 | 631 | 100.0 | 5.0 | 3.9 | 1.1 | 95.0 |
| Russia | 2,112 | 1,341 | 0 | 1,341 | 771 | 100.0 | 63.5 | 0 | 63.5 | 36.5 | 481 | 211 | 0 | 211 | 270 | 100.0 | 43.9 | 0 | 43.9 | 56.1 |
| Spain | 5,537 | 1,272 | 1,028 | 244 | 4,265 | 100.0 | 23.0 | 18.6 | 4.4 | 77.0 | 3,002 | 557 | 351 | 206 | 2,445 | 100.0 | 18.6 | 11.7 | 6.9 | 81.4 |
| Sweden | 2,845 | 780 | 604 | 176 | 2,065 | 100.0 | 27.4 | 21.2 | 6.2 | 72.6 | 4,716 | 3,085 | 157 | 2,928 | 1,631 | 100.0 | 65.4 | 3.3 | 62.1 | 34.6 |
| Switzerland | 4,540 | 3,374 | 2,539 | 835 | 1,166 | 100.0 | 74.3 | 55.9 | 18.4 | 25.7 | 5,645 | 4,315 | 316 | 3,999 | 1,330 | 100.0 | 76.4 | 5.6 | 70.8 | 23.6 |
| Turkey | 2,735 | 70 | 52 | 18 | 2,665 | 100.0 | 2.6 | 1.9 | .7 | 97.4 | 1,110 | 31 | 18 | 13 | 1,079 | 100.0 | 2.8 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 97.2 |
| United Kingdom | 22,800 | 10,895 | 7,823 | 3,072 | 11,905 | 100.0 | 47.8 | 34.3 | 13.5 | 52.2 | 20,093 | 9,522 | 4,008 | 5,514 | 10,571 | 100.0 | 47.4 | 19.9 | 27.4 | 52.6 |
| Other | 3,464 | 120 | 88 | 32 | 3,344 | 100.0 | 3.5 | 2.5 | .9 | 96.5 | 1,927 | 308 | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | 2.7 | A | F |
| Latin America and Other Western Hemisphere |
75,800 | 15,750 | 14,110 | 1,640 | 60,050 | 100.0 | 20.8 | 18.6 | 2.2 | 79.2 | 68,755 | 19,992 | 13,960 | 6,032 | 48,763 | 100.0 | 29.1 | 20.3 | 8.8 | 70.9 |
| Argentina | 3,223 | 408 | 368 | 40 | 2,815 | 100.0 | 12.7 | 11.4 | 1.2 | 87.3 | 1,256 | 147 | 63 | 84 | 1,109 | 100.0 | 11.7 | 5.0 | 6.7 | 88.3 |
| Bahamas | 712 | 107 | 107 | 0 | 605 | 100.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 0 | 85.0 | 605 | 13 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 592 | 100.0 | 2.1 | A | A | 97.9 |
| Brazil | 5,751 | 1,594 | 1,103 | 491 | 4,157 | 100.0 | 27.7 | 19.2 | 8.5 | 72.3 | 7,609 | 2,506 | 1,466 | 1,040 | 5,103 | 100.0 | 32.9 | 19.3 | 13.7 | 67.1 |
| Chile | 2,466 | 186 | 155 | 31 | 2,280 | 100.0 | 7.5 | 6.3 | 1.3 | 92.5 | 1,388 | 140 | 90 | 50 | 1,248 | 100.0 | 10.1 | 6.5 | 3.6 | 89.9 |
| Colombia | 3,286 | 357 | 301 | 56 | 2,929 | 100.0 | 10.9 | 9.2 | 1.7 | 89.1 | 2,837 | 231 | 153 | 78 | 2,606 | 100.0 | 8.1 | 5.4 | 2.7 | 91.9 |
| Costa Rica | 1,357 | 99 | 94 | 5 | 1,258 | 100.0 | 7.3 | 6.9 | .4 | 92.7 | 1,412 | (/D/) | 58 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | 4.1 | A | F |
| Dominican Republic | 2,100 | 63 | 57 | 6 | 2,037 | 100.0 | 3.0 | 2.7 | .3 | 97.0 | 2,373 | (/D/) | 71 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | 3.0 | A | F |
| Ecuador | 999 | 69 | 52 | 17 | 930 | 100.0 | 6.9 | 5.2 | 1.7 | 93.1 | 1,344 | 179 | 139 | 40 | 1,165 | 100.0 | 13.3 | 10.3 | 3.0 | 86.7 |
| El Salvador | 742 | 67 | 62 | 5 | 675 | 100.0 | 9.0 | 8.4 | .7 | 91.0 | 384 | 15 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 369 | 100.0 | 3.9 | A | A | 96.1 |
| Guatemala | 1,205 | 130 | 123 | 7 | 1,075 | 100.0 | 10.8 | 10.2 | .6 | 89.2 | 1,081 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 11 | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | A | 1.0 | F |
| Honduras | 811 | 115 | 113 | 2 | 696 | 100.0 | 14.2 | 13.9 | .2 | 85.8 | 782 | (/D/) | 91 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | 11.6 | A | F |
| Jamaica | 938 | 88 | 80 | 8 | 850 | 100.0 | 9.4 | 8.5 | .9 | 90.6 | 599 | 196 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 403 | 100.0 | 32.7 | B | A | 67.3 |
| Mexico | 40,592 | 10,687 | 10,096 | 591 | 29,905 | 100.0 | 26.3 | 24.9 | 1.5 | 73.7 | 35,211 | 12,209 | 10,739 | 1,470 | 23,002 | 100.0 | 34.7 | 30.5 | 4.2 | 65.3 |
| Netherlands Antilles | 766 | 15 | 12 | 3 | 751 | 100.0 | 2.0 | 1.6 | .4 | 98.0 | 856 | 49 | 5 | 44 | 807 | 100.0 | 5.7 | .6 | 5.1 | 94.3 |
| Panama | 1,103 | 332 | 169 | 163 | 771 | 100.0 | 30.1 | 15.3 | 14.8 | 69.9 | 254 | 35 | 15 | 20 | 219 | 100.0 | 13.8 | 5.9 | 7.9 | 86.2 |
| Peru | 1,005 | 46 | 37 | 9 | 959 | 100.0 | 4.6 | 3.7 | .9 | 95.4 | 738 | (/D/) | 14 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | 1.9 | A | F |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 448 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 1 | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | A | .2 | F | 848 | 475 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 373 | 100.0 | 56.0 | C | A | 44.0 |
| Venezuela | 5,444 | 938 | 870 | 68 | 4,506 | 100.0 | 17.2 | 16.0 | 1.2 | 82.8 | 8,181 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 3,102 | (/D/) | 100.0 | B | A | 37.9 | E |
| Other | 2,852 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 137 | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | A | 4.8 | F | 997 | 363 | 359 | 4 | 634 | 100.0 | 36.4 | 36.0 | .4 | 63.6 |
| Africa | 9,907 | 682 | 306 | 376 | 9,225 | 100.0 | 6.9 | 3.1 | 3.8 | 93.1 | 14,346 | 2,922 | 1,957 | 966 | 11,424 | 100.0 | 20.4 | 13.6 | 6.7 | 79.6 |
| Algeria | 688 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 688 | 100.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100.0 | 1,586 | (/D/) | 0 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | 0 | A | F |
| Angola | 158 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 0 | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | A | 0 | F | 2,303 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 0 | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | A | 0 | F |
| Egypt | 3,088 | 59 | 25 | 34 | 3,029 | 100.0 | 1.9 | .8 | 1.1 | 98.1 | 434 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 0 | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | A | 0 | F |
| Nigeria | 1,001 | 288 | 44 | 244 | 713 | 100.0 | 28.8 | 4.4 | 24.4 | 71.2 | 5,103 | 2,133 | 1,402 | 731 | 2,970 | 100.0 | 41.8 | 27.5 | 14.3 | 58.2 |
| South Africa | 2,434 | 218 | 167 | 51 | 2,216 | 100.0 | 9.0 | 6.9 | 2.1 | 91.0 | 1,727 | 131 | 9 | 122 | 1,596 | 100.0 | 7.6 | .5 | 7.1 | 92.4 |
| Other | 2,538 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 47 | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | A | 1.9 | F | 3,193 | (/D/) | 207 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | 6.5 | A | F |
| Middle East | 16,873 | 679 | 187 | 492 | 16,194 | 100.0 | 4.0 | 1.1 | 2.9 | 96.0 | 15,726 | 4,329 | 579 | 3,750 | 11,397 | 100.0 | 27.5 | 3.7 | 23.K | 72.5 |
| Israel | 4,077 | 116 | 36 | 80 | 3,961 | 100.0 | 2.8 | .9 | 2.0 | 97.2 | 3,815 | 803 | 400 | 403 | 3,012 | 100.0 | 21.0 | 10.5 | 10.6 | 79.0 |
| Kuwait | 1,337 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 65 | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | A | 4.9 | F | 281 | (/D/) | 0 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | 0 | A | F |
| Saudi Arabia | 7,167 | 316 | 14 | 302 | 6,851 | 100.0 | 4.4 | .2 | 4.2 | 95.6 | 10,371 | (/D/) | 1 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | B | (*) | B | E |
| United Arab Emirates | 1,553 | 78 | 69 | 9 | 1,475 | 100.0 | 5.0 | 4.4 | .6 | 95.0 | 812 | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | B | B | A | E |
| Other | 2,739 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 36 | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | A | 1.3 | F | 447 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 2 | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | A | .4 | F |
| Asia and Pacific | 132,070 | 50,786 | 19,365 | 31,421 | 81,284 | 100.0 | 38.5 | 14.7 | 23.8 | 61.5 | 222,502 | 94,802 | 17,185 | 77,617 | 127,700 | 100.0 | 42.6 | 7.7 | 34.9 | 57.4 |
| Australia | 8,876 | 3,062 | 2,788 | 274 | 5,814 | 100.0 | 34.5 | 31.4 | 3.1 | 65.5 | 3,688 | 1,223 | 546 | 677 | 2,465 | 100.0 | 33.2 | 14.8 | 18.4 | 66.8 |
| Bangladesh | 188 | 4 | (*) | 4 | 184 | 100.0 | 2.1 | (*) | 2.1 | 97.9 | 831 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 831 | 100.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100.0 |
| China | 7,418 | 1,456 | 148 | 1,308 | 5,962 | 100.0 | 19.6 | 2.0 | 17.6 | 80.4 | 25,728 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 502 | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | A | 2.0 | F |
| Hong Kong | 9,077 | 3,358 | 2,746 | 612 | 5,719 | 100.0 | 37.0 | 30.3 | 6.7 | 63.0 | 9,793 | 4,823 | 3,481 | 1,342 | 4,970 | 100.0 | 49.2 | 35.5 | 13.7 | 50.8 |
| India | 1,917 | 78 | 18 | 60 | 1,839 | 100.0 | 4.1 | .9 | 3.1 | 95.9 | 3,780 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 20 | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | A | .5 | F |
| Indonesia | 2,779 | 305 | 163 | 142 | 2,474 | 100.0 | 11.0 | 5.9 | 5.1 | 89.0 | 4,529 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 119 | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | A | 2.6 | F |
| Japan | 47,813 | 33,525 | 7,592 | 25,933 | 14,288 | 100.0 | 70.1 | 15.9 | 54.2 | 29.9 | 97,414 | 69,447 | 1,991 | 67,456 | 27,967 | 100.0 | 71.3 | 2.0 | 69.2 | 28.7 |
| Korea, Republic of | 14,639 | 1,970 | 631 | 1,339 | 12,669 | 100.0 | 13.5 | 4.3 | 9.1 | 86.5 | 16,682 | 3,761 | 264 | 3,497 | 12,921 | 100.0 | 22.5 | 1.6 | 21.0 | 77.5 |
| Malaysia | 4,363 | 857 | 744 | 113 | 3,506 | 100.0 | 19.6 | 17.1 | 2.6 | 80.4 | 8,294 | 2,671 | 2,151 | 520 | 5,623 | 100.0 | 32.2 | 25.9 | 6.3 | 67.8 |
| New Zealand | 1,307 | 209 | 180 | 29 | 1,098 | 100.0 | 16.0 | 13.8 | 2.2 | 84.0 | 1,218 | 262 | 24 | 238 | 956 | 100.0 | 21.5 | 2.0 | 19.5 | 78.5 |
| Pakistan | 881 | (/D/) | 12 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | 1.4 | A | F | 866 | 0 | (*) | 0 | 866 | 100.0 | 0 | (*) | 0 | 100.0 |
| Philippines | 2,759 | 192 | 126 | 66 | 2,567 | 100.0 | 7.0 | 4.6 | 2.4 | 93.0 | 4,355 | 611 | 337 | 274 | 3,744 | 100.0 | 14.0 | 7.7 | 6.3 | 86.0 |
| Singapore | 9,626 | 3,109 | 2,485 | 624 | 6,517 | 100.0 | 32.3 | 25.8 | 6.5 | 67.7 | 11,313 | 7,573 | 6,023 | 1,550 | 3,740 | 100.0 | 66.9 | 53.2 | 13.7 | 33.1 |
| Taiwan | 15,250 | 1,791 | 1,053 | 738 | 13,459 | 100.0 | 11.7 | 6.9 | 4.8 | 88.3 | 24,596 | 1,985 | 881 | 1,104 | 22,611 | 100.0 | 8.1 | 3.6 | 4.5 | 91.9 |
| Thailand | 3,989 | 813 | 658 | 155 | 3,176 | 100.0 | 20.4 | 16.5 | 3.9 | 79.6 | 7,529 | 1,075 | 762 | 313 | 6,454 | 100.0 | 14.3 | 10.1 | 4.2 | 85.7 |
| Other | 1,188 | (/D/) | 21 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | 1.8 | A | F | 1,886 | 15 | 11 | 5 | 1,871 | 100.0 | .8 | .6 | .3 | 99.2 |
| Unallocated | 623 | 61 | 562 | 727 | 0 | 727 | ||||||||||||||
D Suppressed to avoid the disclosure of data of individual companies.
* Less than $500,000 or less than 0.05 percent, as appropriate.
1. Data are from the Bureau of the Census.
NOTES.—The countries listed in this table are the 62 U.S. trading partners for which the sum of U.S. exports and U.S. imports was at least $1 billion in 1992.
Size ranges are given in the percentage cells that are suppressed; these ranges are A—0.01 to 19.9; B—20.0 to 39.9; C—40.0 to 59.9; E—60.0 to 79.9; F—80.0 to 100.
| Millions of dollars | Percent | |||||||
| All industries | Manufacturing | Wholesale trade | Petroleum and other industries |
All industries | Manufacturing | Wholesale trade | Petroleum and other industries |
|
| Exports by country of destination: |
||||||||
| All countries | 100,737 | 65,272 | 31,501 | 3,964 | 100.0 | 64.8 | 31.3 | 3.9 |
| Canada | 33,878 | 28,177 | 5,285 | 416 | 100.0 | 83.2 | 15.6 | 1.2 |
| Europe | 32,829 | 17,335 | 13,769 | 1,725 | 100.0 | 52.8 | 41.9 | 5.3 |
| Belgium and Luxembourg | 2,598 | 1,626 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | 62.6 | B | A |
| France | 3,975 | 1,830 | 2,058 | 87 | 100.0 | 46.0 | 51.8 | 2.2 |
| Germany | 6,544 | 4,423 | 1,969 | 152 | 100.0 | 67.6 | 30.1 | 2.3 |
| Ireland | 834 | 778 | 54 | 2 | 100.0 | 93.3 | 6.5 | .2 |
| Italy | 1,614 | 876 | 716 | 22 | 100.0 | 54.3 | 44.4 | 1.4 |
| Netherlands | 4,412 | 2,115 | 1,939 | 358 | 100.0 | 47.9 | 43.9 | 8.1 |
| Spain | 1,028 | 495 | 523 | 10 | 100.0 | 48.2 | 50.9 | 1.0 |
| Sweden | 604 | 156 | 440 | 8 | 100.0 | 25.8 | 72.8 | 1.3 |
| Switzerland | 2,539 | 185 | 2,321 | 33 | 100.0 | 7.3 | 91.4 | 1.3 |
| United Kingdom | 7,823 | 4,533 | 2,449 | 841 | 100.0 | 57.9 | 31.3 | 10.8 |
| Other | 858 | 318 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | 37.1 | C | A |
| Latin America and Other Western Hemisphere |
14,110 | 11,700 | 1,487 | 923 | 100.0 | 82.9 | 10.5 | 6.5 |
| Brazil | 1,103 | 1,064 | 19 | 20 | 100.0 | 96.5 | 1.7 | 1.8 |
| Mexico | 10,096 | 9,335 | 672 | 89 | 100.0 | 92.5 | 6.7 | .9 |
| Venezuela | 870 | 678 | 164 | 28 | 100.0 | 77.9 | 18.9 | 3.2 |
| Other | 2,041 | 623 | 632 | 786 | 100.0 | 30.5 | 31.0 | 38.5 |
| Africa | 306 | 147 | 67 | 92 | 100.0 | 48.0 | 21.9 | 30.1 |
| Nigeria | 44 | 13 | 8 | 23 | 100.0 | 29.5 | 18.2 | 52.3 |
| Other | 262 | 134 | 59 | 69 | 100.0 | 51.1 | 22.5 | 26.3 |
| Middle East | 187 | 23 | 57 | 107 | 100.0 | 12.3 | 30.5 | 57.2 |
| Asia and Pacific | 19,365 | 7,890 | 10,835 | 640 | 100.0 | 40.7 | 56.0 | 3.3 |
| Australia | 2,788 | 1,186 | 1,549 | 53 | 100.0 | 42.5 | 55.6 | 1.9 |
| Hong Kong | 2,746 | 581 | 2,102 | 63 | 100.0 | 21.2 | 76.5 | 2.3 |
| Indonesia | 163 | 26 | 15 | 122 | 100.0 | 16.0 | 9.2 | 74.8 |
| Japan | 7,592 | 2,408 | 4,929 | 255 | 100.0 | 31.7 | 64.9 | 3.4 |
| Korea, Republic of | 631 | 406 | 206 | 19 | 100.0 | 64.3 | 32.6 | 3.0 |
| Malaysia | 744 | 599 | 145 | (*) | 100.0 | 80.5 | 19.5 | (*) |
| Singapore | 2,485 | 1,530 | 897 | 58 | 100.0 | 61.6 | 36.1 | 2.3 |
| Taiwan | 1,053 | 513 | 517 | 23 | 100.0 | 48.7 | 49.1 | 2.2 |
| Thailand | 658 | 457 | 187 | 14 | 100.0 | 69.5 | 28.4 | 2.1 |
| Other | 505 | 184 | 288 | 33 | 100.0 | 36.4 | 57.0 | 6.5 |
| Unallocated | 61 | 61 | ||||||
| Imports by country of origin: |
||||||||
| All countries | 83,260 | 67,241 | 7,803 | 8,216 | 100.0 | 80.8 | 9.4 | 9.9 |
| Canada | 36,613 | 31,789 | 1,166 | 3,658 | 100.0 | 86.8 | 3.2 | 10.0 |
| Europe | 12,967 | 9,956 | 2,498 | 513 | 100.0 | 76.8 | 19.3 | 4.0 |
| Belgium and Luxembourg | (/D/) | (/D/) | 109 | 1 | 100.0 | F | A | A |
| France | 1,829 | 890 | 933 | 6 | 100.0 | 48.7 | 51.0 | .3 |
| Germany | 2,558 | 2,431 | 91 | 36 | 100.0 | 95.0 | 3.6 | 1.4 |
| Ireland | 1,053 | 1,037 | 16 | 0 | 100.0 | 98.5 | 1.5 | 0 |
| Italy | 616 | 492 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | 79.9 | A | A |
| Netherlands | 891 | 781 | 94 | 16 | 100.0 | 87.7 | 10.5 | 1.8 |
| Spain | 351 | 257 | 94 | (*) | 100.0 | 73.2 | 26.8 | (*) |
| Sweden | 157 | 155 | 2 | (*) | 100.0 | 98.7 | 1.3 | (*) |
| Switzerland | 316 | 73 | 242 | 1 | 100.0 | 23.1 | 76.6 | .3 |
| United Kingdom | 4,008 | 2,923 | 802 | 283 | 100.0 | 72.9 | 20.0 | 7.1 |
| Other | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | E | A | B |
| Latin America and Other Western Hemisphere |
14,770 | 12,271 | 543 | 1,956 | 100.0 | 83.1 | 3.7 | 13.2 |
| Brazil | 1,466 | 1,464 | (*) | 2 | 100.0 | 99.9 | 0 | .1 |
| Mexico | 10,739 | 10,423 | 266 | 50 | 100.0 | 97.1 | 2.5 | .5 |
| Venezuela | (/D/) | 9 | 1 | (/D/) | 100.0 | E | A | B |
| Other | (/D/) | 375 | 276 | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | A | E |
| Africa | 1,957 | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | A | F |
| Nigeria | 1,402 | 0 | 0 | 1,402 | 100.0 | 0 | 0 | 100.0 |
| Other | 554 | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | A | F |
| Middle East | 579 | (/D/) | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | E | A | B |
| Asia and Pacific | 17,185 | 12,776 | 3,576 | 833 | 100.0 | 74.3 | 20.8 | 4.8 |
| Australia | 546 | 363 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | 66.5 | B | A |
| Hong Kong | 3,481 | 867 | 2,609 | 5 | 100.0 | 24.9 | 74.9 | .1 |
| Indonesia | (/D/) | 5 | 0 | (/D/) | 100.0 | A | 0 | F |
| Japan | 1,991 | 1,447 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | 72.7 | B | A |
| Korea, Republic of | 264 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 0 | 100.0 | F | A | 0 |
| Malaysia | 2,151 | 2,150 | 1 | 0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | (*) | 0 |
| Singapore | 6,023 | 5,777 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | 95.9 | A | A |
| Taiwan | 881 | 829 | 50 | 2 | 100.0 | 94.1 | 5.7 | .2 |
| Thailand | 762 | (/D/) | 1 | (/D/) | 100.0 | F | .1 | A |
| Other | (/D/) | 405 | 1 | (/D/) | 100.0 | F | A | A |
D Suppressed to avoid the disclosure of data of individual companies.
* Less than $500,000 or less than .05 percent, as appropriate.
NOTES.—The countries listed in this table are the U.S. trading partners in table 6 for which intrafirm U.S. exports to or imports from majority-owned foreign affiliates was at least $500 million in 1992.
Size ranges are given in the percentage cells that are suppressed; these ranges are A—0.1 to 19.9; B—20.0 to 39.9; C—40.0 to 59.9; E—60.0 to 79.9; F—80.0 to 100.
| Millions of dollars | Percent | Addendum: Percentage of U.S.-affiliate intrafirm trade with country accounted for by affiliates with UBO's in the country |
|||||||
| All industries | Manufacturing | Wholesale trade | Petroleum and other industries |
All industries | Manufacturing | Wholesale trade | Petroleum and other industries |
||
| Exports by country of destination: |
|||||||||
| All countries | 48,767 | 11,574 | 34,612 | 2,581 | 100.0 | 23.7 | 71.0 | 5.3 | |
| Canada | 3,606 | 2,166 | 1,130 | 310 | 100.0 | 60.1 | 31.3 | 8.6 | 38.9 |
| Europe | 10,671 | 4,934 | 5,136 | 601 | 100.0 | 46.2 | 48.1 | 5.6 | |
| Belgium and Luxembourg | 455 | 301 | 101 | 53 | 100.0 | 66.2 | 22.2 | 11.6 | 20.2 |
| France | 972 | 728 | 153 | 91 | 100.0 | 74.9 | 15.7 | 9.4 | 64.4 |
| Germany | 1,902 | 1,286 | 499 | 117 | 100.0 | 67.6 | 26.2 | 6.2 | 66.8 |
| Italy | 446 | 187 | 189 | 70 | 100.0 | 41.9 | 42.4 | 15.7 | 62.8 |
| Netherlands | 800 | 463 | 301 | 36 | 100.0 | 57.9 | 37.6 | 4.5 | 48.9 |
| Russia | 1,341 | 1 | 1,341 | 0 | 100.0 | .1 | 100.0 | 0 | 0 |
| Sweden | 176 | 125 | 36 | 15 | 100.0 | 71.0 | 20.5 | 8.5 | 68.2 |
| Switzerland | 835 | 655 | 166 | 14 | 100.0 | 78.4 | 19.9 | 1.7 | 73.1 |
| United Kingdom | 3,072 | 874 | 2,049 | 149 | 100.0 | 28.5 | 66.7 | 4.9 | 30.9 |
| Other | 672 | 314 | 301 | 56 | 100.0 | 46.7 | 44.8 | 8.3 | |
| Latin America and Other Western Hemisphere |
1,640 | 477 | 721 | 442 | 100.0 | 29.1 | 44.0 | 27.0 | |
| Brazil | 491 | 81 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | 16.5 | A | E | E |
| Mexico | 591 | 259 | 311 | 21 | 100.0 | 43.8 | 52.6 | 3.6 | 34.0 |
| Venezuela | 68 | 35 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | 51.5 | A | B | A |
| Other | 490 | 102 | 346 | 42 | 100.0 | 20.8 | 70.6 | 8.6 | |
| Africa | 376 | 123 | 80 | 173 | 100.0 | 32.7 | 21.3 | 46.0 | |
| Nigeria | 244 | (/D/) | 0 | (/D/) | 100.0 | B | 0 | E | 0 |
| Other | 132 | 28 | 80 | 24 | 100.0 | 21.2 | 60.6 | 18.2 | |
| Middle East | 492 | 20 | 124 | 348 | 100.0 | 4.1 | 25.2 | 70.7 | |
| Saudi Arabia | 302 | 2 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | .7 | A | F | F |
| Other | 190 | 18 | 121 | 51 | 100.0 | 9.5 | 63.7 | 26.8 | |
| Asia and Pacific | 31,421 | 3,489 | 27,262 | 670 | 100.0 | 11.1 | 86.8 | 2.1 | |
| Australia | 274 | 182 | 59 | 33 | 100.0 | 66.4 | 21.5 | 12.0 | 18.6 |
| China | 1,308 | 38 | 1,242 | 28 | 100.0 | 2.9 | 95.0 | 2.1 | C |
| Hong Kong | 612 | 374 | 203 | 35 | 100.0 | 61.1 | 33.2 | 5.7 | 4.7 |
| Japan | 25,933 | 2,350 | 23,240 | 343 | 100.0 | 9.1 | 89.6 | 1.3 | 97.6 |
| Korea, Republic of | 1,339 | 38 | 1,203 | 98 | 100.0 | 2.8 | 89.8 | 7.3 | 72.4 |
| Malaysia | 113 | 45 | 68 | 0 | 100.0 | 39.8 | 60.2 | 0 | A |
| Singapore | 624 | 197 | 367 | 60 | 100.0 | 31.6 | 58.8 | 9.6 | 2.6 |
| Taiwan | 738 | 198 | 510 | 30 | 100.0 | 26.8 | 69.1 | 4.1 | 27.8 |
| Other | 480 | 67 | 370 | 43 | 100.0 | 14.0 | 77.1 | 9.0 | |
| Unallocated | 562 | 364 | 158 | 40 | |||||
| Imports by country of origin: |
|||||||||
| All countries | 137,799 | 37,259 | 89,202 | 11,338 | 100.0 | 27.0 | 64.7 | 8.2 | |
| Canada | 9,448 | 4,311 | 3,538 | 1,599 | 100.0 | 45.6 | 37.4 | 16.9 | 70.0 |
| Europe | 39,259 | 17,417 | 20,248 | 1,594 | 100.0 | 44.4 | 51.6 | 4.1 | |
| Belgium and Luxembourg | 1,767 | 598 | 1,077 | 92 | 100.0 | 33.8 | 61.0 | 5.2 | 31.6 |
| France | 3,888 | 2,085 | 1,592 | 211 | 100.0 | 53.6 | 40.9 | 5.4 | 79.4 |
| Germany | 14,880 | 6,069 | 8,542 | 269 | 100.0 | 40.8 | 57.4 | 1.8 | 93.7 |
| Italy | 1,291 | 457 | 653 | 181 | 100.0 | 35.4 | 50.6 | 14.0 | 77.4 |
| Netherlands | 2,530 | 1,038 | 1,451 | 41 | 100.0 | 41.0 | 57.4 | 1.6 | 82.2 |
| Russia | 211 | 0 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | 0 | F | A | F |
| Sweden | 2,928 | 599 | 2,291 | 38 | 100.0 | 20.5 | 78.2 | 1.3 | 95.7 |
| Switzerland | 3,999 | 3,006 | 975 | 18 | 100.0 | 75.2 | 24.4 | .5 | 75.1 |
| United Kingdom | 5,514 | 2,455 | 2,402 | 657 | 100.0 | 44.5 | 43.6 | 11.9 | 80.0 |
| Other | 2,251 | 1,110 | 1,056 | 85 | 100.0 | 49.3 | 46.9 | 3.8 | |
| Latin America and Other Western Hemisphere |
6,032 | 605 | 1,814 | 3,613 | 100.0 | 10.0 | 30.1 | 59.9 | |
| Brazil | 1,040 | 217 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | 20.9 | B | C | 66.8 |
| Mexico | 1,470 | 342 | 1,099 | 29 | 100.0 | 23.3 | 74.8 | 2.0 | 38.7 |
| Venezuela | 3,102 | (*) | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | (*) | A | F | F |
| Other | 420 | 46 | 308 | 66 | 100.0 | 11.0 | 73.3 | 15.7 | |
| Africa | 966 | 129 | 87 | 750 | 100.0 | 13.4 | 9.0 | 77.6 | |
| Nigeria | 731 | 0 | (/D/) | (/D/) | 100.0 | 0 | A | F | 0 |
| Other | 235 | 129 | 79 | 27 | 100.0 | 54.9 | 33.6 | 11.5 | |
| Middle East | 3,750 | 68 | 207 | 3,475 | 100.0 | 1.8 | 5.5 | 92.7 | |
| Saudi Arabia | 3,331 | 0 | 0 | 3,331 | 100.0 | 0 | 0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | 419 | 68 | 207 | 144 | 100.0 | 16.2 | 49.4 | 34.4 | |
| Asia and Pacific | 77,617 | 14,394 | 62,929 | 294 | 100.0 | 18.5 | 81.1 | .4 | |
| Australia | 677 | 117 | 523 | 37 | 100.0 | 17.3 | 77.3 | 5.5 | 43.1 |
| China | 502 | 68 | 419 | 15 | 100.0 | 13.5 | 83.5 | 3.0 | E |
| Hong Kong | 1,342 | 218 | 1,086 | 38 | 100.0 | 16.2 | 80.9 | 2.8 | 30.2 |
| Japan | 67,456 | 12,149 | 55,153 | 154 | 100.0 | 18.0 | 81.8 | .2 | 99.5 |
| Korea, Republic of | 3,497 | 507 | 2,968 | 22 | 100.0 | 14.5 | 84.9 | .6 | 92.6 |
| Malaysia | 520 | 283 | 237 | 0 | 100.0 | 54.4 | 45.6 | 0 | 0 |
| Singapore | 1,550 | 310 | 1,239 | 1 | 100.0 | 20.0 | 79.9 | .1 | 2.6 |
| Taiwan | 1,104 | 331 | 761 | 12 | 100.0 | 30.0 | 68.9 | 1.1 | 62.6 |
| Other | 969 | 411 | 543 | 15 | 100.0 | 42.4 | 56.0 | 1.5 | |
| Unallocated | 727 | 336 | (/D/) | (/D/) | |||||
D Suppressed to avoid the disclosure of data of individual companies.
* Less than $500,000 or less than .05 percent, as appropriate.
NOTES.—The countries listed in this table are the U.S. trading partners in table 6 for which intrafirm exports or imports by U.S. affiliates was at least $500 million in 1992.
Size ranges are given in the percentage cells that are suppressed; these ranges are A—0.1 to 19.9; B—20.0 to 39.9; C—40.0 to 59.9; E—60.0 to 79.9; F—80.0 to 100.
Imports.—The intrafirm-trade share of U.S. imports also varied substantially across countries. Among the top six source-countries for U.S. imports—Canada, Japan, Mexico, Germany, China, and Taiwan—the share ranged from 71 percent for Japan to less than 10 percent for China and Taiwan (table 6, column 7). For Germany, the share was 61 percent. In addition to Japan and Germany, intrafirm trade accounted for a majority of U.S. imports from seven other countries; the share was highest for Switzerland (76 percent). In addition to China and Taiwan, intrafirm trade accounted for less than 10 percent of U.S. imports from 19 other countries.
For slightly more than one-half of the countries shown in table 6, imports by U.S. affiliates from their foreign parent groups accounted for a majority of U.S. intrafirm imports. The share of total U.S. imports that was accounted for by U.S.-affiliate intrafirm imports (26 percent) was much higher than the share accounted for by U.S. intrafirm imports from MOFA's (16 percent). This difference in shares reflects the large U.S.-affiliate shares for a few countries, including some of the largest source-countries for U.S. imports: Intrafirm imports by U.S. affiliates accounted for 69 percent of U.S. imports from Japan and 52 percent of U.S. imports from Germany (table 6, column 9). The shares were also very large for Switzerland (71 percent), Sweden (62 percent), and the Netherlands (48 percent). The imports from Switzerland were mainly by manufacturing affiliates (particularly affiliates in the pharmaceutical industry), and the imports from Japan, Germany, Sweden, and the Netherlands were mainly by wholesale trade affiliates (table 8)./21/ For Germany and Sweden, a large share of the imports were by wholesale trade affiliates of motor vehicle companies headquartered in those countries.
Intrafirm imports from MOFA's accounted for a substantial share of U.S. imports from a number of major trading partners, including Canada, Mexico, and three rapidly industrializing countries in Southeast Asia—Singapore, Hong Kong, and Malaysia (table 6, column 8). The shares were particularly high for Singapore (53 percent) and Canada (37 percent). Most of the intrafirm imports from Canada and Mexico were from manufacturing affiliates, particularly affiliates in the motor vehicle industry (table 7). Manufacturing affiliates also accounted for virtually all of the intrafirm imports from Singapore and Malaysia; most of these imports were from MOFA's in the computer and electronic components industries. In contrast, the intrafirm imports from Hong Kong were mainly from MOFA's in wholesale trade.
Intrafirm transactions—particularly shipments flowing from parent companies to their affiliates—tend to be relatively more important in U.S. trade with higher income countries. Among 59 major trading partners, there is a pronounced tendency for the shares of both U.S.-MNC intrafirm exports in total U.S. exports and foreign-MNC intrafirm imports in total U.S. imports to increase as the per capita gross national product (GNP) of the trading partners increases (table 9). For U.S.-MNC intrafirm trade, the average share of U.S. exports increases from 4 percent for the 11 trading partners with a per capita GNP of less than $1,000 to 23 percent for the 14 trading partners with a per capita GNP of at least $20,000. For foreign-MNC intrafirm trade, the average share of U.S. imports increases from less than 3 percent for the 11 countries with the lowest per capita GNP to 35 percent for the 14 countries with the highest per capita GNP.
| Number of countries |
Intrafirm trade of U.S. MNC's | Intrafirm trade of foreign MNC's | |||
| As a percentage of U.S. exports to country |
As a percentage of U.S. imports from country |
As a percentage of U.S. exports to country |
As a percentage of U.S. imports from country |
||
| All countries | 59 | 13.0 | 10.8 | 6.2 | 14.5 |
| GNP per capita (U.S. dollars): | |||||
| 20,000 or more | 14 | 22.6 | 10.7 | 9.9 | 35.1 |
| 10,000 to 19,999 | 9 | 22.1 | 21.7 | 4.5 | 13.4 |
| 2,000 to 9,999 | 15 | 9.6 | 10.5 | 7.9 | 12.9 |
| 1,000 to 1,999 | 10 | 5.9 | 6.8 | 1.2 | 2.3 |
| Less than 1,000 | 11 | 4.3 | 6.1 | 5.3 | 2.6 |
NOTES.—Countries are grouped by their per capita GNP. The average intrafirm-trade shares shown are unweighted averages for all countries in a given size group.
The 59 countries consist of all of the trading partners shown in table 6 except the Netherlands Antilles, Angola, and Kuwait (countries for which 1992 data on per capita GNP are not available).
The data on GNP per capita for all of the countries except Taiwan are from the World Bank, World Development Report, 1994. For Taiwan, the U.S.-dollar value of GNP per capita, from Taiwan Government sources, was provided by the International Trade Administration.
GNP Gross national product
1. The country category "international" consists of affiliates that have operations spanning more than one country and that are engaged in petroleum shipping, other water transportation, or offshore oil and gas drilling.
The positive relation between the intrafirm-trade shares and trading-partner income levels partly reflects shipments by parent firms to their wholesale trade affiliates: The shares in trade of both exports by U.S. parent companies to their wholesale trade MOFA's and imports by U.S. wholesale trade affiliates from their foreign parent groups are strongly correlated with the per capita GNP of U.S. trading partners (table 10). A local presence in overseas markets through the establishment of wholesale trade affiliates—and the associated replacement of arm's-length transactions with intrafirm trade—is often required for the marketing of sophisticated, heterogeneous manufactured products (such as automobiles and advanced machinery products), which tend to be both supplied from and sold to higher income countries./22/
| U.S. exports to country | U.S. imports from country | |||
| Coefficient of correlation across 59 countries between per capita GNP and the percentage of U.S. exports to or imports from country accounted for by: | ||||
| Total intrafirm trade | 0.601 | *** | 0.672 | *** |
| Intrafirm trade between U.S. parent companies and their majority-owned foreign affiliates: | ||||
| Affiliates in all industries | .659 | *** | .122 | |
| Manufacturing affiliates | .332 | ** | .183 | |
| Wholesale trade affiliates | .731 | *** | .240 | * |
| Affiliates in petroleum and other industries | -.191 | -.135 | ||
| Intrafirm trade between U.S. affiliates and their foreign parent groups: | ||||
| Affiliates in all industries | .211 | .709 | *** | |
| Manufacturing affiliates | .649 | *** | .716 | *** |
| Wholesale trade affiliates | .077 | .588 | *** | |
| Affiliates in petroleum and other industries | -.062 | -.077 | ||
*** Statistically significant at the 99-percent confidence level.
** Statistically significant at the 95-percent confidence level.
* Statistically significant at the 90-percent confidence level.
NOTE.—The sample of 59 countries consists of all of the trading partners shown in table 6 except the Netherlands Antilles, Angola, and Kuwait (see note to table 9).
GNP Gross national product
For U.S. MNC's, most intrafirm trade is between U.S. parents and their manufacturing MOFA's. The share of U.S. exports accounted for by intrafirm exports to manufacturing MOFA's is positively correlated with the per capita GNP of U.S. trading partners; however, the relation is not as strong as that for intrafirm exports to wholesale trade MOFA's. The positive correlation is consistent with the fact that U.S.-MNC manufacturing production is largely concentrated in high-income countries: In 1992, 74 percent of the gross product of manufacturing MOFA's was accounted for by MOFA's in Canada and Europe. Among the 59 trading partners, Canada and several high-income countries in Europe had the highest shares of U.S. exports accounted for by intrafirm exports to manufacturing MOFA's. The share was also sizable for a few middle-income countries (most notably Mexico and Brazil), but it was generally very small for low-income countries.
In contrast, the share of U.S. imports accounted for by intrafirm imports from manufacturing MOFA's is not significantly related to the per capita GNP of the trading partners. This result reflects the local-market orientation of U.S. multinational production in most high-income countries: The intrafirm share of imports, in contrast to that of exports, is substantially lower for a number of high-income countries in Europe, where affiliates produce mainly for the local market, and substantially higher for the several middle-income countries where affiliates tend to export much of their output to the United States./23/ Like intrafirm exports, intrafirm imports from manufacturing affiliates generally account for a small share of U.S. imports from the trading partners with the lowest incomes. If some U.S. companies rely extensively on low-income countries for production operations requiring low-skilled labor, it would appear that the associated trade flows commonly take the form of market transactions with unrelated parties rather than intrafirm trade.
For foreign MNC's, the share of U.S. imports accounted for by intrafirm imports by U.S. manufacturing affiliates is strongly correlated with the per capita GNP of U.S. trading partners, reflecting the fact that foreign direct investment in U.S. manufacturing has come largely from high-income countries. Much of this investment has been in advanced manufacturing industries, such as chemicals or electronic equipment, where firms might be expected to possess some proprietary technology. In such industries, the parent firms may produce specialized materials or components that they then supply to their affiliates through intrafirm trade./24/
Although the correlation for the share of intrafirm exports by manufacturing affiliates is also positive and significant, the overall correlation for intrafirm exports by U.S. affiliates is insignificant, because of the very weak correlation for wholesale trade affiliates (which account for the bulk of U.S.-affiliate trade). The insignificant correlation for exports by wholesale trade affiliates partly reflects intrafirm exports to lower income countries by French-owned trading companies.
1. For a discussion of the worldwide surge in direct investment after 1985, see Edward M. Graham and Paul R. Krugman, "The Surge in Foreign Direct Investment in the 1980s," in Foreign Direct Investment, edited by Kenneth A. Froot (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1993): 13–36. For examples of the attention given to intrafirm trade by international organizations, which have shown particular interest in this phenomenon, see United Nations Conference on Trade and Development, Division on Transnational Corporations and Investment, World Investment Report 1995 (New York: United Nations, 1995): Chapter IV; and Marcos Bonturi and Kiichiro Fukasaku, "Globalization and Intra-firm Trade: An Empirical Note," in OECD Economic Studies 20 (Spring 1993): 145–159.
2. See "An Ownership-Based Disaggregation of the U.S. Current Account, 1982–93," SURVEY OF CURRENT BUSINESS 75 (October 1995): 52–61.
3. As shown in the October 1995 article, trade in goods has consistently accounted for more than 80 percent of U.S. intrafirm exports of goods and services and for more than 90 percent of U.S. intrafirm imports of goods and services.
4. The UBO is that person, proceeding up a U.S. affiliate's ownership chain, beginning with and including the foreign parent, that is not owned more than 50 percent by another person. "Person" is broadly defined to include any individual, corporation, branch, partnership, associated group, association, estate, trust, or other organization and any government (including any corporation, institution, or other entity or instrumentality of a government). The foreign parent is the first foreign person in the affiliate's ownership chain. Unlike the foreign parent, the UBO of an affiliate is identified to ascertain the person that ultimately owns or controls the U.S. affiliate and that, therefore, ultimately derives the benefits from owning or controlling the affiliate.
5. The data for 1994 are preliminary.
6. The foreign parent group consists of (1) the foreign parent, (2) any foreign person, proceeding up the foreign parent's ownership chain, that owns more than 50 percent of the person below it, up to and including the UBO, and (3) any foreign person, proceeding down the ownership chain(s) of each of these members, that is owned more than 50 percent by the person above it.
7. The increase in share in 1982–85, when the dollar was appreciating in world currency markets, and the subsequent decrease in share in 1985–89, when the dollar was depreciating, might suggest that intrafirm exports were less sensitive to exchange-rate changes than were "arm's-length" exports (that is, exports involving unaffiliated parties). For 1985–89, however, Subramanian Rangan and Robert Z. Lawrence have determined that the apparent insensitivity at the aggregate level is due to industry-mix effects, so that once industry mix is taken into account, there is virtually no difference between the growth rates of intrafirm exports and of arm's-length exports; see "The Responses of U.S. Firms to Exchange Rate Fluctuations: Piercing the Corporate Veil," Brookings Papers on Economic Activity 2 (1993): 341–379.
8. In 1977, imports from petroleum affiliates accounted for 42 percent of the total goods imported by U.S. parents from their foreign affiliates. Although total U.S. imports of petroleum and products increased $17 billion from 1977 to 1982, imports by U.S. parents from petroleum affiliates decreased from $13.8 billion to $12.6 billion, and intrafirm imports from petroleum affiliates located in the member countries of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries dropped from $7.9 billion to $5.0 billion.
9. The data on the intended use of U.S. goods exported to majority-owned foreign affiliates are collected in BEA's benchmark survey of U.S. direct investment abroad. In each of the most recent benchmark survey years—1982, 1989, and 1994—at least three-fourths of the exports by U.S. parents to their majority-owned manufacturing affiliates were goods for further manufacture by the affiliates. In contrast, more than 90 percent of the intrafirm exports to majority-owned affiliates in wholesale trade were goods for resale without further manufacture.
10. The data on the intended use of U.S. goods imported by foreign-owned U.S. affiliates are collected in BEA's benchmark surveys of foreign direct investment in the United States. In each of the benchmark survey years—1980, 1987, and 1992—more than 90 percent of the imports received by U.S. wholesale trade affiliates from their foreign parent groups were goods for resale. In contrast, goods for resale accounted for less than one-third of the intrafirm imports by manufacturing affiliates.
11. In BEA's annual surveys of U.S. direct investment abroad, intrafirm-trade data by industry and by country of affiliate are collected only for MOFA's. (The data on intrafirm trade with all foreign affiliates, not broken down by industry or country of affiliate, are collected on reports for U.S. parent companies.) In 1977 and 1982–94, intrafirm trade between U.S. parents and their MOFA's accounted for more than 90 percent of the intrafirm exports to, and for more than 85 percent of the intrafirm imports from, all foreign affiliates.
12. In each of the most recent benchmark survey years—1982, 1989, and 1992—machinery exports accounted for more than one-half of the intrafirm exports to MOFA's in wholesale trade. (Data on U.S. trade with MOFA's by product are collected only in benchmark survey years.)
13. Japan's largest general trading companies have historically handled a substantial share of Japan's imports of bulk commodities from other countries. See Alexander K. Young, The Sogo Shosha: Japan's Multinational Trading Companies (Boulder, Colorado: Westview Press, 1979).
14. The share of total U.S. goods imports that was accounted for by the intrafirm imports by U.S. manufacturing affiliates also increased—from 4 percent in 1985 to 7 percent in 1992. The share of intrafirm exports by U.S. manufacturing affiliates increased from 1 percent in 1977 to 3 percent in 1994.
15. In 1977–94, the share for affiliates in chemicals remained in the range of 27 to 37 percent for exports and 18 to 22 percent for imports. The share for affiliates in electronic equipment was less stable, fluctuating in the range of 12 to 30 percent for exports and 17 to 25 percent for imports.
16. During 1987–90, the share of Japanese-owned manufacturing affiliates in the gross product of all manufacturing affiliates doubled—from 6 percent to 12 percent.
17. The data for intrafirm trade of U.S. affiliates are from the 1992 benchmark survey of foreign direct investment in the United States. Data on U.S.-affiliate trade by country of destination and by country of origin are collected in benchmark surveys, but not in annual surveys.
18. In this section, as in the previous section, total intrafirm trade is defined as the sum of the intrafirm trade between U.S. parents and MOFA's and the intrafirm trade between U.S. affiliates and their foreign parent groups (see footnote 11).
19. Intrafirm trade between a U.S. affiliate and its foreign parent group need not be trade with the country of the affiliate's UBO, because some member firms of the foreign parent group may be located in other countries.
20. Exports to France accounted for only 15 percent of the intrafirm exports by French-owned affiliates.
21. As shown in the addendum to table 8, the U.S.-affiliate intrafirm imports from these five countries were predominantly by affiliates with UBO's in those countries. In addition, imports originating in the UBO country accounted for a dominant share of the intrafirm imports by affiliates with UBO's in all of the countries except the Netherlands: Imports from the UBO country accounted for more than 90 percent of the intrafirm imports by Japanese- and German-owned affiliates and for more than 70 percent of the intrafirm imports by Swiss- and Swedish-owned affiliates.
22. As mentioned earlier, these products may require the establishment of wholesale trade affiliates to monitor customer requirements or tastes and to provide on-site after-sales service.
23. To illustrate this contrast, the share of U.S. goods trade with Germany that is accounted for by intrafirm trade with manufacturing MOFA's is 21 percent for exports and 8 percent for imports. For U.S. trade with Malaysia, the shares are 14 percent for exports and 26 percent for imports. According to 1992 data from BEA's annual survey of U.S. direct investment abroad, the share of sales that were to the United States was 3 percent for manufacturing MOFA's in Germany and 56 percent for manufacturing MOFA's in Malaysia.
24. Although most foreign direct investment in the United States has taken the form of acquisitions of existing companies rather than the establishment of new companies, the reliance of foreign-owned manufacturing affiliates on their foreign parents for intermediate products is considerable: In 1992, intrafirm imports accounted for 12 percent of the total purchased inputs of U.S. manufacturing affiliates.